FIGURE 1.
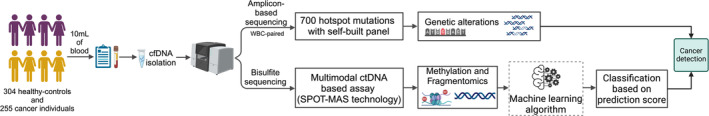
Diagram illustrates study design. Our study recruited 304 healthy controls and 255 cancer participants. From each participant, 10 mL of blood was drawn. Cell‐free DNA (cfDNA) and genomic DNA (gDNA) were isolated for targeted sequencing using a 700‐hotspot mutation panel. Mutation calling was performed, with CHIP mutations filtered out to confirm positive mutations. Another fraction of cfDNA was subjected to the SPOT‐MAS assay, which uses bisulfite sequencing to profile methylomic and fragmentomic features for classification analysis by machine learning algorithms. The detection abilities of the hotspot mutation‐based approach and the SPOT‐MAS‐based approach were evaluated individually and in combination.
