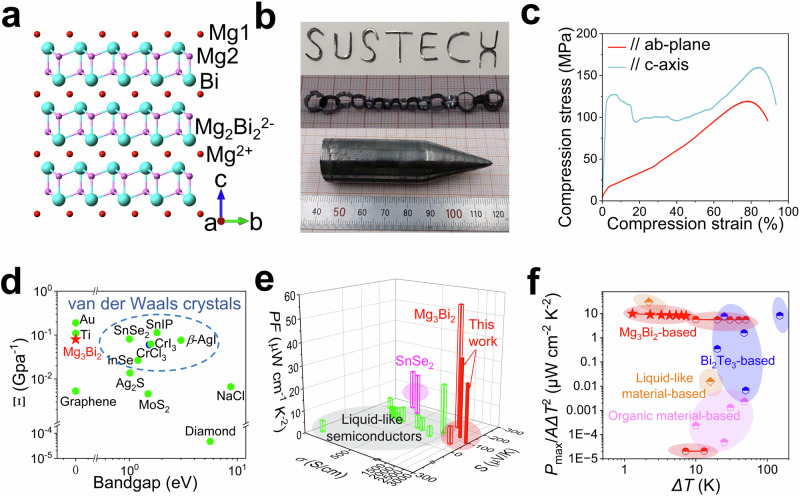
Fig. 1. Structure, plasticity, and thermoelectric properties of α-Mg3Bi2 single crystals.
a Crystal structure of α-Mg3Bi2, in which Mg atoms occupy two distinct lattice sites (Mg1 and Mg2). The atom arrangement of α-Mg3Bi2 comprises periodic small-sized Mg2+ interlayers and covalent bonded Mg2Bi22− networks. b An as-grown n-type α-Mg3Bi2 crystal, the letters “SUSTECH” and a flexible chain deformed by crystal slabs. c Uniaxial compression experiments. α-Mg3Bi2 crystals sustained >90% compression strain. d Deformability factor Ξ of α-Mg3Bi2 and several other materials (listed in Supplementary Table 1)30,32,34,35. e Room-temperature power factors for inorganic plastic inorganic semiconductors (listed in Supplementary Table 2)6,20–29,31,39. The electrical transport performance of α-Mg3Bi2 was better than that of liquid-like plastic inorganic semiconductors and van der Waals semiconductors. f Normalized power density (Pmax/AΔT2) of out-of-plane flexible thermoelectric devices (listed in Supplementary Table 3)6,9,40–50, including α-Mg3Bi2 based40,41, liquid-like material-based6,50, Bi2Te3-based42–46, and organic material-based9,47–49 devices. Our data are marked by red stars.