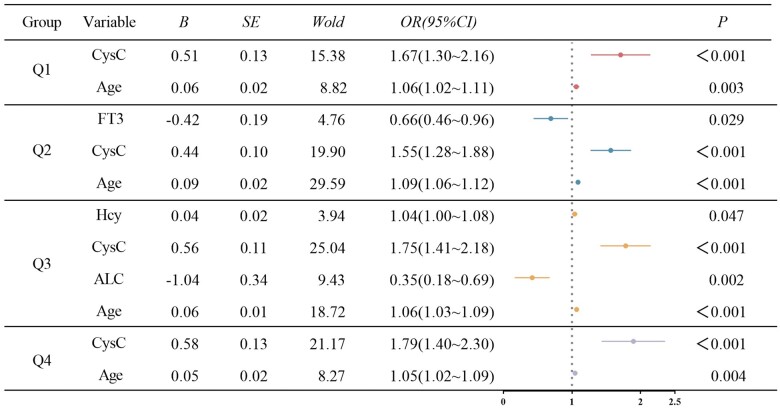
Figure 5.
Logistic regression analysis of risk factors related to renal function abnormalities in patients with gout with different serum urate levels. Age and cystatin C (CysC) were risk factors for gout combined with abnormal renal function in the Q1 group. In the Q2 group, age and CysC were risk factors for gout combined with abnormal renal function, and serum-free triiodothyronine (FT3) was a protective factor. In the Q3 group, age, CysC and homocysteine (Hcy) were risk factors for gout associated with abnormal renal function, and absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) was a protective factor. In the Q4 group, age and CysC were risk factors for gout combined with abnormal renal function. Variables include: gender, age, haemoglobin (HGB), platelet count (PLT), neutrophil percentage (NE%), percentage lymphocytes (LY%), percentage monocytes (MO%), absolute neutrophil count (ANC), ALC, mean corpuscular haemoglobin content (MCH), mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC), alanine transaminase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum urate (UA), cystatin C (CysC), triglycerides (TG), cholesterol (CHOL), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC), apolipoprotein A (APOA), apolipoprotein B (APOB), lipoprotein A (LPA), Hcy, FT3, serum-free tetraiodothyronine (FT4) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)