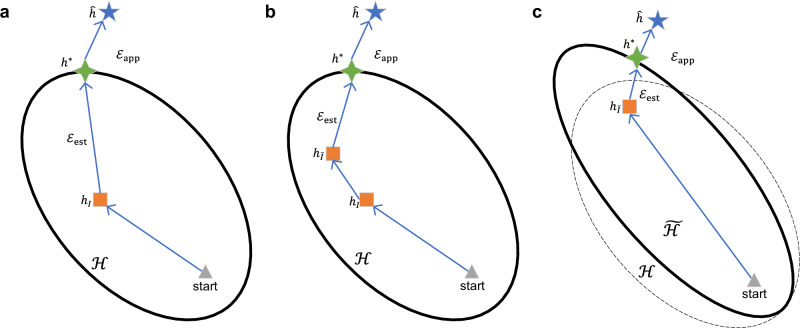
Fig. 4. Illustration of error decomposition and the approach of Electron Configuration models with Stacked Generalization (ECSG) to limited data problems.
a Decomposition of error between expected risk and empirical risk. (b, c) show how ECSG solves limited data problems by augmenting data and restricting hypothesis space using domain knowledge. Triangles represent starting points; the blue stars () denote the optimal hypothesis; the green four-pointed stars () and the orange squares () represent the hypotheses that minimize expected risk and empirical risk, respectively, within hypothesis space . The area enclosed by the dotted line () and correspond to the hypothesis space and the resulting hypothesis after incorporating diverse knowledge sources. refers to the error between the optimal hypothesis in and the global hypothesis, while represents the error between or and .