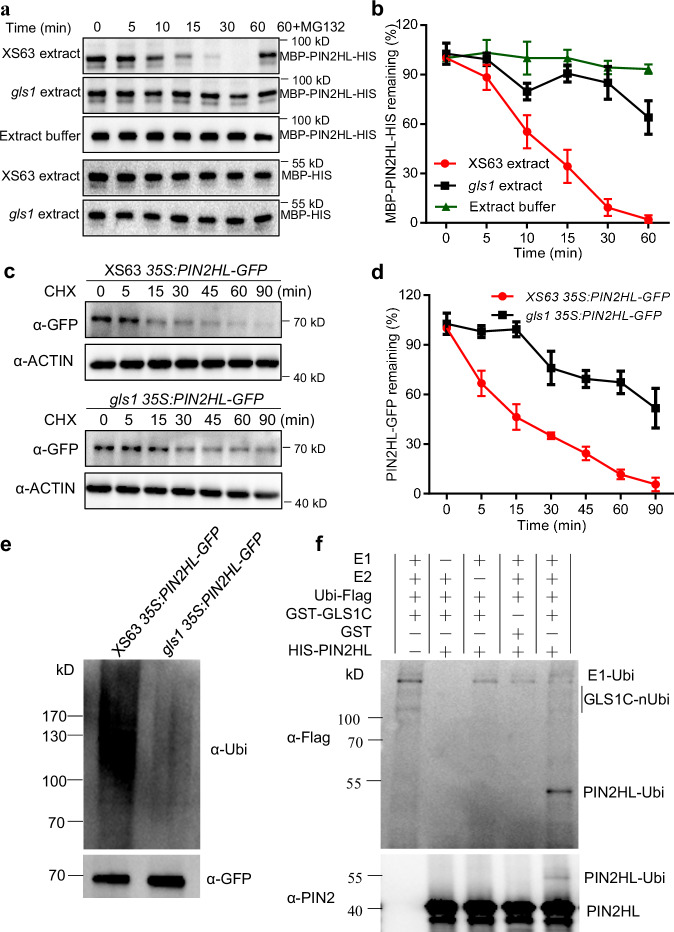
Fig. 5. OsGLS1 directly ubiquitinates and degrades OsPIN2 in vitro and in vivo.
OsPIN2HL degradation in cell-free degradation assays. Total proteins extracted from the roots of XS63 or gls1 seedlings were incubated with recombinant MBP-PIN2HL-HIS alone or with MG132 for the indicated times; MBP-PIN2HL-HIS was detected using anti-MBP antibody (a); the band signal intensity was quantified (b). MBP-HIS was used as a control. c, d Regulation of OsPIN2HL stability by OsGLS1 in vivo. Total proteins were extracted from the roots of 10-day-old seedlings from 35S:PIN2HL-GFP in XS63 and gls1 35S:PIN2HL-GFP transgenic lines treated with 100 μM cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times. PIN2HL-GFP was detected using anti-GFP antibody (c) and band signal intensity quantified (d). OsACTIN1 was used as a loading control. In b and d, data represent means ± SD (n = 3). e In vivo ubiquitination assay of OsGLS1 on OsPIN2HL. The roots of 10-day-old seedlings from 35S:PIN2HL-GFP in XS63 and gls1 35S:PIN2HL-GFP transgenic lines treated with 50 μM MG132 for 8 h were sampled for protein extraction. PIN2HL-GFP was immunoprecipitated using anti-GFP antibody-conjugated beads. Ubiquitinated PIN2HL-GFP was detected using an anti-ubiquitin antibody (α-Ubi). f Ubiquitination of OsPIN2HL by OsGLS1 in vitro. Recombinant HIS-PIN2HL was incubated with GST-GLS1C alone or in the presence of E1, E2 and ubiquitin-Flag (Ubi-Flag). Ubiquitinated HIS-PIN2HL was detected using anti-Flag and anti-PIN2 antibodies.