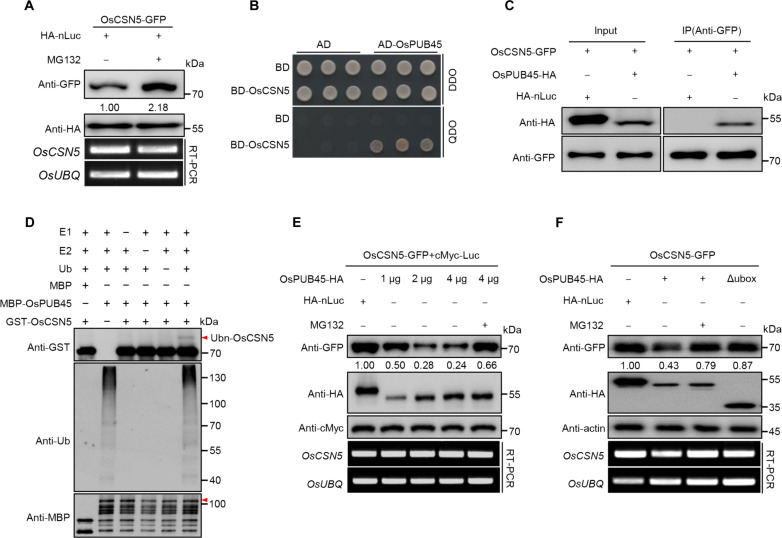
Fig. 2. OsPUB45 ubiquitinates and targets OsCSN5 for degradation via the 26S proteasome pathway.
(A) OsCSN5-GFP abundance was detected in transfected protoplasts after treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide or MG132. OsCSN5-GFP was then detected by immunoblotting with an anti-GFP antibody. HA-nLuc serves as a loading control. The relative transcript levels of OsCSN5 and OsUBQ were detected by RT-PCR. (B) OsPUB45 interacts with OsCSN5 in yeast. AD, pGADT7 AD vector; BD, pGBKT7 BD vector. Yeast were grown on DDO (SD-Leu-Trp) or QDO (SD-Leu-Trp-His-Ade) medium. (C) Co-IP assay for the interaction between OsCSN5 and OsPUB45 in rice protoplasts. OsCSN5-GFP was coexpressed with HA-nLuc and OsPUB45-HA in rice protoplasts. (D) Ubiquitination assay of OsCSN5 by OsPUB45 in vitro. GST-OsCSN5 from Escherichia coli was incubated with E1, E2, Ub, and rice total extract preincubated MBP-OsPUB45 in the reactions. Ubiquitination of GST-OsCSN5 was detected by anti-GST antibody. Ubn-OsCSN5 denotes ubiquitinated OsCSN5 band. (E) Degradation of OsCSN5 is OsPUB45 dosage dependent. OsCSN5-GFP was coexpressed with HA-nLuc, OsPUB45-HA in rice protoplasts, respectively. Numbers under the bands indicate relative OsCSN5-GFP abundance, normalized to cMyc-Luc as loading control. The relative transcript levels of OsCSN5 and OsUBQ were detected by RT-PCR. Similar results were obtained from three independent biological experiments. (F) OsPUB45 promotes the degradation of OsCSN5 via 26S proteasome pathway in vivo. OsCSN5-GFP was cotransfected with HA-nLuc, OsPUB45-HA, or OsPUB45-Δubox-HA in rice protoplasts, respectively. Actin serves as an internal control. The relative transcript levels of OsCSN5 and OsUBQ were detected by RT-PCR. Similar results were obtained from three independent biological experiments.