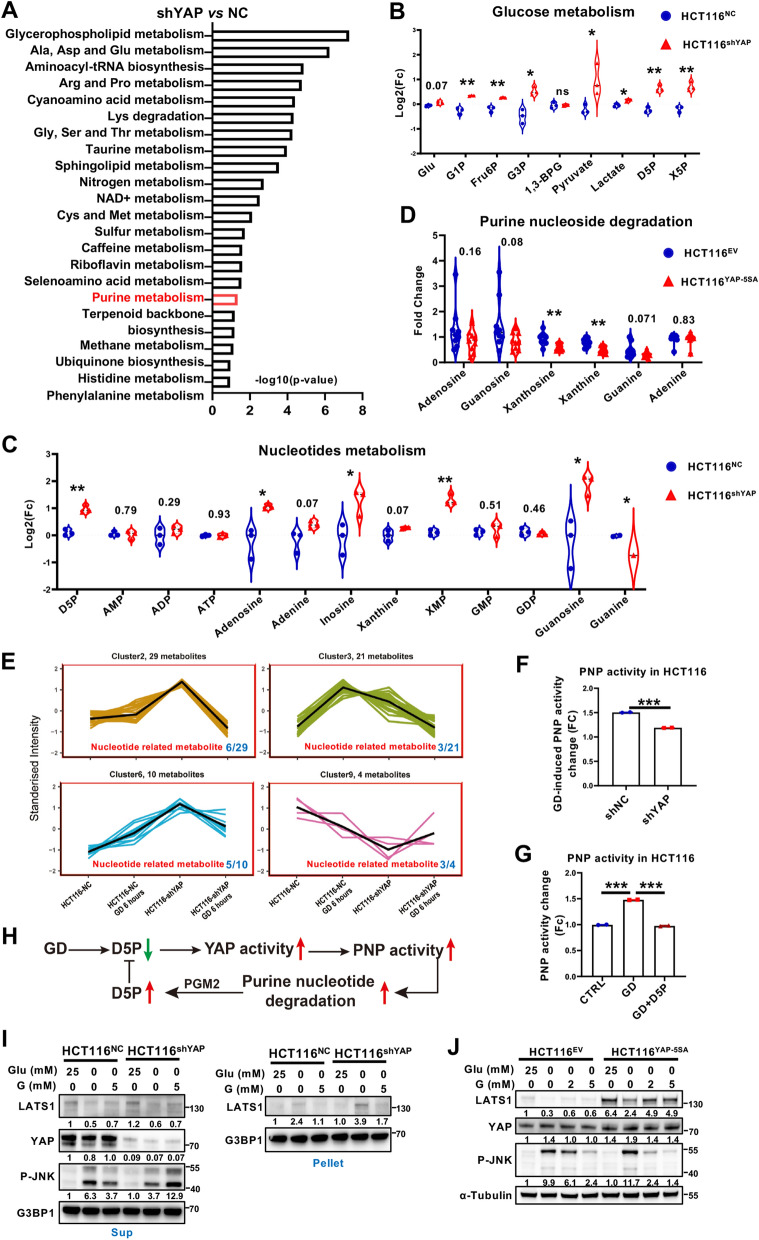
Fig. 5.
Dysregulation of YAP activity reprograms purine nucleotide metabolism and cellular response to GD. A Set enrichment of polar metabolites from HCT116-shYAP and HCT116-NC cells as determined by 600MRM analysis. B Relative levels of metabolites involved in glucose metabolism in HCT116-NC and HCT116-shYAP cells. C Relative levels of metabolites involved in purine (adenine and guanine) nucleotide metabolism in HCT116-NC and HCT116-shYAP cells. D Relative levels of metabolites involved in purine (adenine and guanine) nucleotide metabolism in HCT116-EV- and HCT116-YAP-5SA-overexpressing cells. E Cluster analysis of polar metabolites of HCT116-NC and HCT116-shYAP cells under normal culture or GD conditions (0 mM, 6 h). F Analysis of PNP enzyme activity in HCT116-NC and HCT116-shYAP cells treated under GD. G Analysis of PNP enzyme activity in HCT116 cells treated under GD with or without D5P supplementation. H Schematic diagram depicting that GD-induced D5P downregulation triggers YAP activation, promoting PNP activity to recover D5P level. I Immunoblotting analysis of LATS1, YAP and phosphorylated JNK in the supernatants (Sup) or LATS1 in the pellets of HCT116-NC and HCT116-shYAP cells under the indicated treatment. G3BP1 was used as a loading control. J Immunoblotting analysis of LATS1, YAP and phosphorylated JNK in the supernatants of HCT116-EV- and YAP-5SA-overexpressing cells with the indicated treatment. Tubulin was used as a loading control. The experiments in (I), (J) were repeated twice independently. In (B–D) and (F–G), data are the mean ± S.D.; P values were calculated using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significance