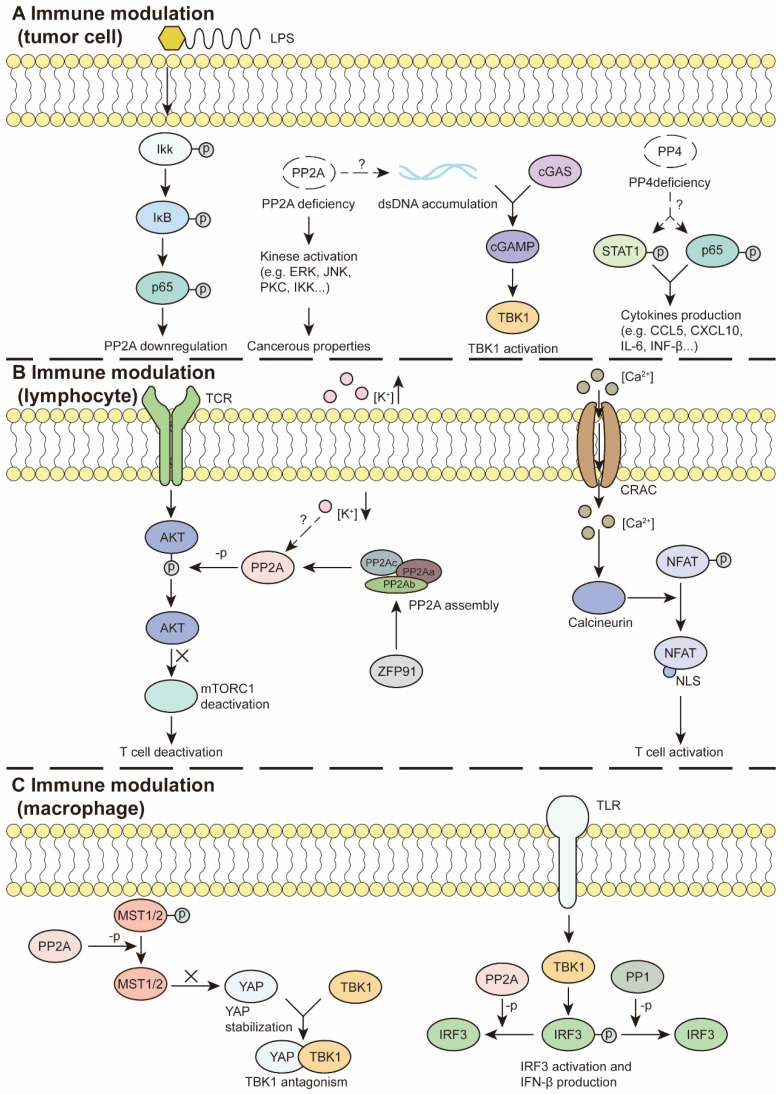
Figure 4.
PSPs in immune modulation. (A) In tumor cells, inflammatory factors, such as LPS activate NF-κB pathway and reduce PP2A expression. PP2A deficiency promotes kinase activation and acquires cancerous properties. PP2A deficiency activates the GAS-STING pathway to modulate immunity. PP4 deficiency facilitates STAT1 and P65 activation and cytokine production. (B) In lymphocytes, PP2A can inhibit TCR-induced mTORC1 activation and T cell activation. Moreover, elevation of the extracellular k+ concentration can suppress T cell functions, which is required for intact PP2A. ZFP91 promotes PP2A holoenzyme assembly and downstream effects. Besides, Ca2+ flows through the iron channel CRAC and activates calcineurin, which dephosphorylates NFAT and exposes the NLS. Activated NFAT regulates T cell activation. (C) In macrophages, TLR/TBK/IRF3 pathway promotes IFN-β production, whereas PP1 or PP2A can interrupt the process by IRF3 dephosphorylation. Additionally, PP2A dephosphorylates MST1/2 to stabilize YAP, which antagonizes TBK1 and its subsequent effects. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide, NLS: nuclear localization signal, ZFP91: Zinc finger protein 91