FIGURE 7.
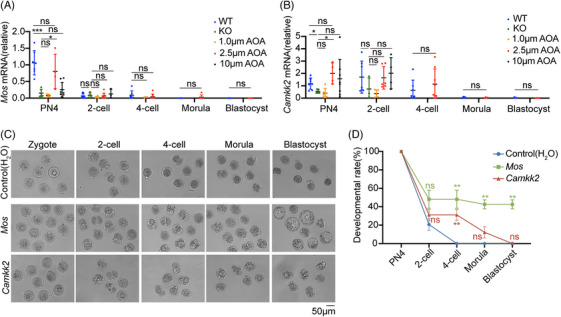
Fertilization with Tdrd6−/− sperm causes abnormal expression of Mos in zygotes and consequent early embryonic arrest. (A) qRT‐PCR results showing the relative expression of Mos at different stages of embryonic development after intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) with sperm from wild‐type (WT) or Tdrd6−/− mice or after intracytoplasmic sperm injection‐artificial oocyte activation (ICSI‐AOA) with different concentrations of ionomycin. Each circle represents a separate embryo. The bars indicate the mean ± SEMs. n = 3 biologically independent male mice in each group. (B) qRT‐PCR was used to determine the relative expression of Camkk2 during different stages of embryonic development after ICSI with sperm from WT or Tdrd6−/− mice or after ICSI‐AOA with different concentrations of ionomycin. Each circle represents a separate embryo. The bars indicate the mean ± SEMs. n = 3 biologically independent male mice in each group. (C) Representative images of embryonic development at different stages after Tdrd6−/− zygotes were injected with H2O (control), Mos, or Camkk2 mRNA. Scale bars, 50 µm. (D) Quantification of embryonic development at different stages after Tdrd6−/− zygotes were injected with H2O (control), Mos, or Camkk2 mRNA. The bars indicate the mean ± SEMs. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001. n = 3 biologically independent male mice in each group.
