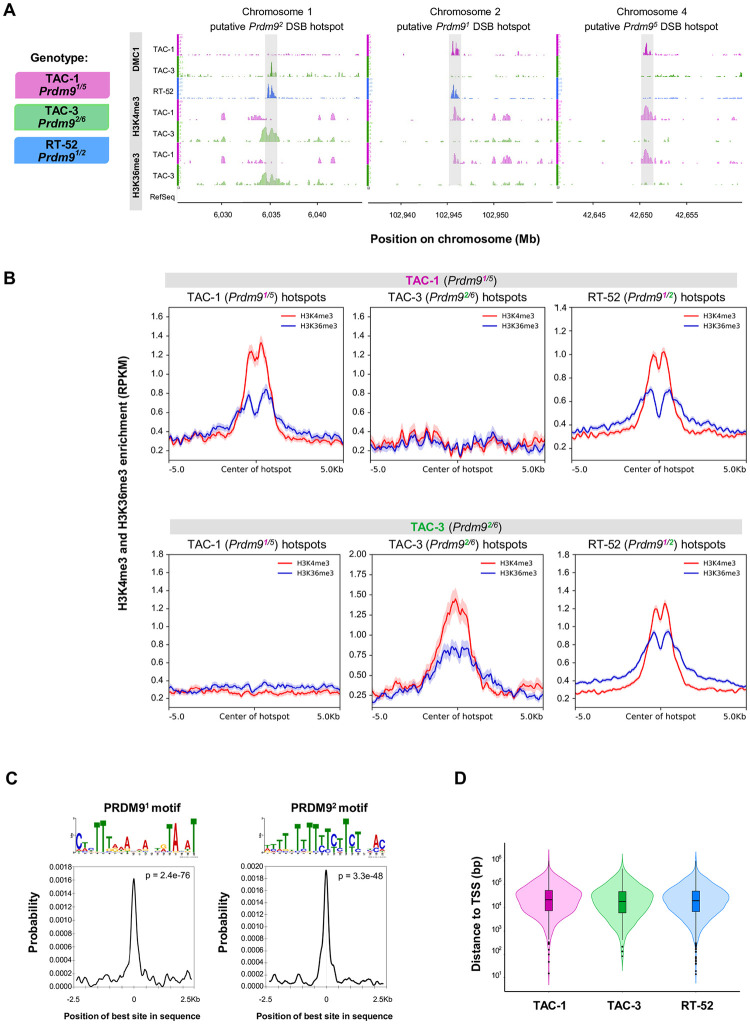
Fig 3. Meiotic DSB hotspots are specified by full length PRDM9 in O. mykiss.
(A) DSB hotspots detected by DMC1-SSDS (DMC1), H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 in selected regions of the O. mykiss genome in testes from 2 or 3 (DMC1) individuals. (B) Average profile of H3K4me3 (red) and H3K36me3 (blue) ChIP-seq signal in TAC-1 (Prdm91/5) and TAC-3 (Prdm92/6) testes, at DSB hotspots detected in TAC-1 (Prdm91/5), TAC-3 (Prdm92/6), and RT-52 (Prdm91/2). (C) On top, the PRDM9 allele 1 (E = 5.1e-37) and allele 2 motifs (E = 1.2e-63) discovered in allele 1 (n = 300) and allele 2 DSB sites (n = 254) are shown. Below, the plots depict the distribution of hits for the PRDM9 allele 1 (left) and allele 2 (right) motifs at allele 1 and allele 2 DSB sites from the center of the sequence up to 2.5 kb of distance. The signal is smoothed by weighted moving average, and hits were calculated in a 250 bp sliding window. (D) Violin plot showing the distribution of DSB hotspots from TAC-1 (magenta), TAC-3 (green), and RT-52 (blue) relative to the TSS from RefSeq annotated genes. The data and codes underlying this figure can be found in https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11083953 and https://zenodo.org/records/14198863. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; DSB, double-strand break; TSS, transcription start site.