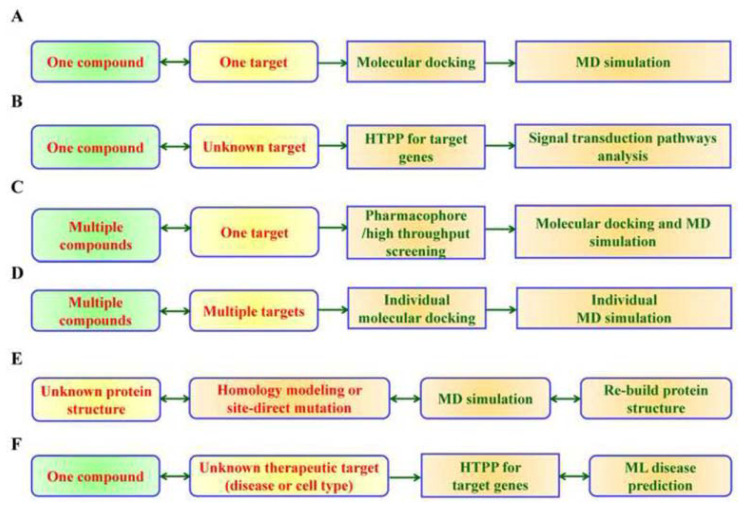
Fig. 4.
Pipeline of In Silico R&D platforms for various disease models at NPRL. Each component (A–F) showed a distinct computational approach for analyzing compounds and targets. (A) Single-compound single-target model: Molecular docking was used to test a single compound against a specific target, and MD simulation was used to improve the interaction analysis. (B) Single compound unknown target model: HTPP is used to identify possible target genes for compounds with unknown targets. A signal transduction pathway analysis is added to clarify the compound's mode of action. (C) Multiple compound-single target model: pharmacophore modeling or high-throughput screening tests of a group of compounds against a single target. Molecular docking and MD simulations are then used for a more in-depth analysis. (D) The multiple compound-multiple target model tests different compounds against different targets. Molecular docking and MD simulations improve the connection between each compound and its target. (E) Homology Modeling and site-directed mutation prediction model: Homology modeling or site-directed mutagenesis was used for proteins with unknown structures or mutations. This is followed by MD simulations and protein structure reconstruction. (F) Therapeutic Target Identification Model: If the compound's therapeutic target (disease or cell type) is unknown, HTPP is used to guess the target genes. ML techniques are used to treat diseases.