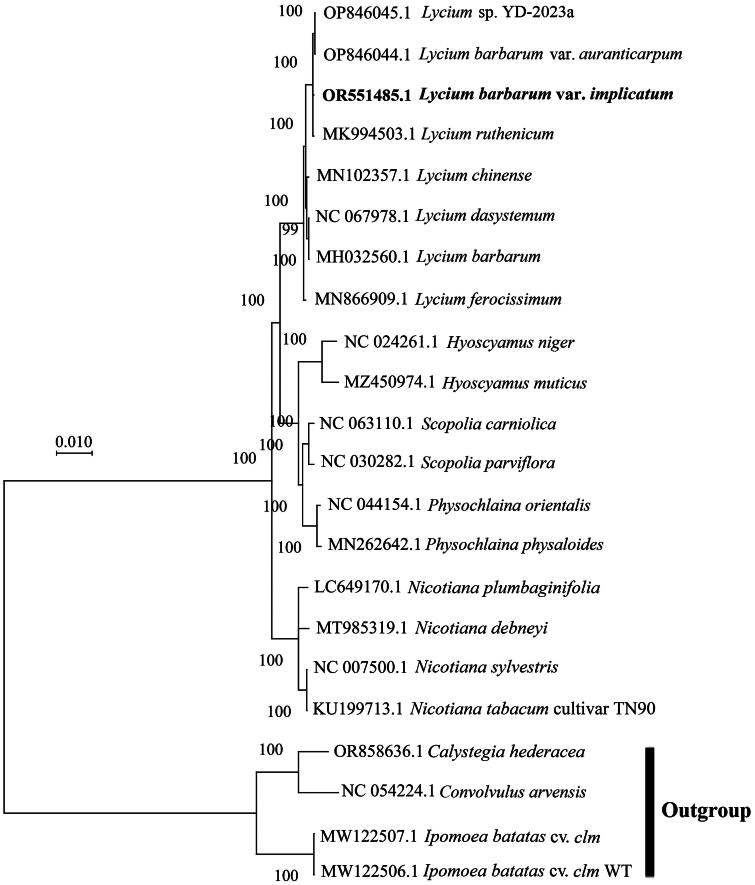
Figure 4.
Maximum-likelihood (ML) tree generated with 17 complete cp genomes related to L. barbarum var. implicatum and four outgroups. Bootstrap values are shown near the nodes, and the bold font represents the cp genome of L. barbarum var. implicatum in this study. The following sequences, some of which are stored in the NCBI database and most of which remain unpublished, were used: L. dasystemum (NC 067978), Hyoscyamus niger (NC 024261), Scopolia carniolica (NC 063110), S. parviflora (NC 030282), Physochlaina orientalis (NC 044154), Nicotiana sylvestris (NC 007500), Convolvulus arvensis (NC 054224) (Wang et al. 2021), N.tabacum (KU 199713) (Gao et al. 2016), N. plumbaginifolia (LC 649170) (Tong et al. 2022), L. barbarum (MH032560) (Jia et al. 2018), L. ruthenicum (MK994503) (Wang et al. 2019), L. chinense (MN102357) (He et al. 2020), L. ferocissimum (MN866909) (Li et al. 2020), P. physaloides (MN 262642) (Tong et al. 2019), N.debneyi (MT985319) (Zeng et al. 2021), Ipomoea batatas (MW122506, MW122507) (Zou et al. 2021), H. muticus (MZ 450974), Lycium sp. (OP846045), L. barbarum var. auranticarpum (OP846044) and Calystegia hederacea (or 858636).