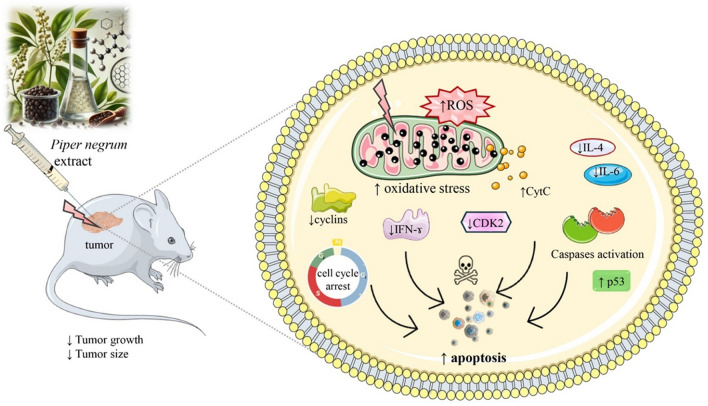
Fig. 2.
Apoptosis molecular mechanisms of Piper nigrum extract (PNE). PNE administration leads to decreased tumor size and growth, primarily through the induction of oxidative stress via increased ROS levels, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction and CytC release. This process activates caspases and p53, promoting apoptosis. PNE also causes cell cycle arrest by reducing the expression of cyclins and CDK2. Additionally, PNE modulates inflammatory responses by lowering IL-4, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels, contributing to its anticancer effects. CDK2: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, a cell cycle regulatory protein; CytC: Cytochrome c, released from mitochondria during apoptosis; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma, a cytokine involved in immune regulation; IL-4: Interleukin-4, an anti-inflammatory cytokine; IL-6: Interleukin-6, a pro-inflammatory cytokine; p53: A tumor suppressor protein involved in apoptosis regulation; PNE: Piper nigrum extract; ROS: Reactive oxygen species, molecules causing oxidative stress; ↓decrease, ↑increase