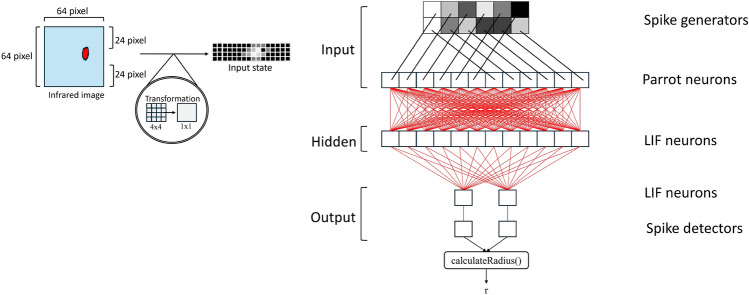
Fig. 3.
Encoding strategy of an infrared image input and its SNN architecture, as introduced in [96]. The input data from the infrared camera is resized to simplify data processing and then converted into spike form for input to the neural networks. The SNN structure consists of 64 input neurons, with the intensity of each pixel normalized and used to determine the average firing rate of the spike generator encoding the input image. The SNN controller generates steering commands for a snake-like robot. The spike output of the neural networks is interpreted as motor control commands, with the spike signal decoded to control the robot’s slithering locomotion