Table 2.
Brief description of isotherm models used for both metal ions adsorption onto modified ACF at a dosage of 0.5 g/L and pH 5.0 for Cu(II) and cd(II) at 298 K.
| Metals | Langmuir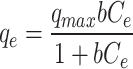
|
Freundlich
|
Temkin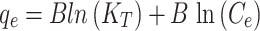
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) |
KL (L/mg) |
R2 | KF (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n | n (L/g) (L/g) |
R2 | KT (L/mg) | B (J/mol) | R2 | |
| Cd(II) | 214.590 | 0.092 | 0.9850 | 38.521 | 2.700 | 0.9948 | 101.990 | 13.990 | 0.8933 |
| Cu(II) | 163.390 | 0.047 | 0.9681 | 18.268 | 2.267 | 0.9728 | 24.052 | 1.846 | 0.9780 |
Here, Cedenotes the metal ion concentration at equilibrium (mg/L); qe and qmax represent the equilibrium and maximum adsorption capacities of the metal ion (mg/g), respectively. The coefficients KL, KF, and KTcorrespond to the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models, respectively. Parameter n is a constant that describes the linearity of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm related to the adsorption heat in the Temkin isotherm. Additionally, R2is the correlation coefficient.
