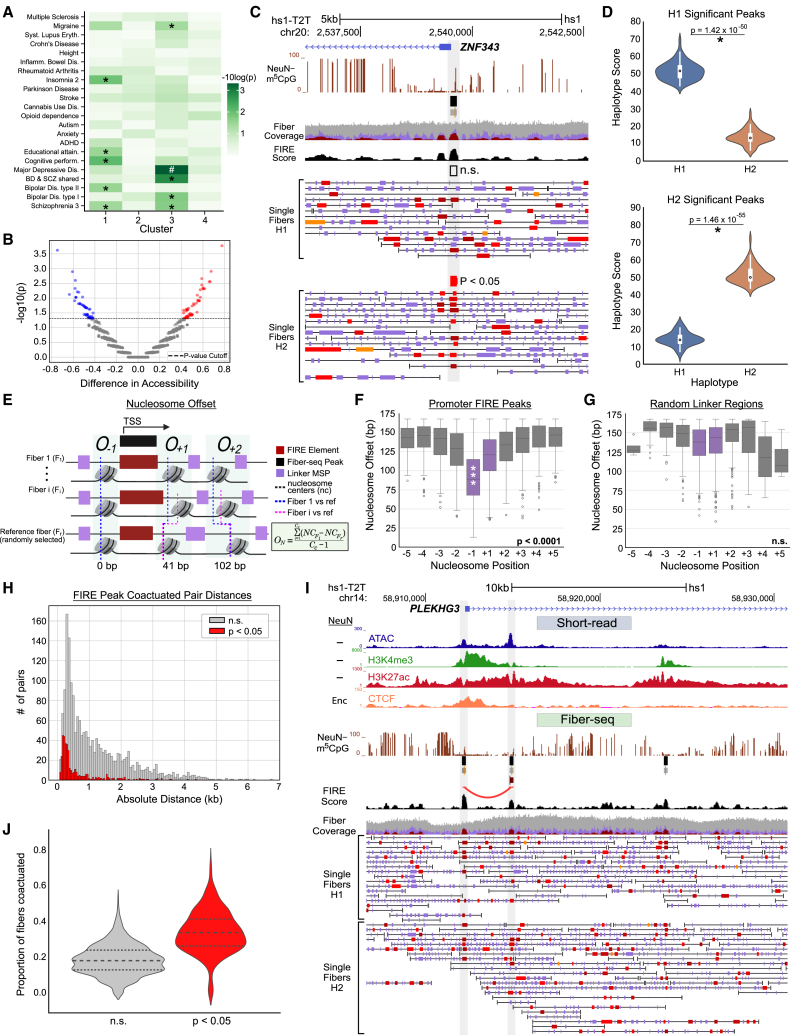
Figure 4.
Nucleosomes show sequence-specific fixation proximal to accessible TSS
(A) Enrichment of brain-specific traits based on the identity of GWAS-locus-specific SNPs in each cluster of Fiber-seq-called peaks, excluding peaks located at repetitive regions. Significant traits are labeled with ∗ (p < 0.05) and # (p < 0.01).
(B) Volcano plot of Fiber-seq peaks with haplotype-specific differences (N = 3,708), with the difference in accessibility on the x axis and the −log10 p value on the y axis. Peaks with nominal p < 0.05 by a Fisher test are colored red (H1 high) and blue (H2 high).
(C) UCSC genome browser visualization of fiber-to-fiber variability including a significantly haplotype differential Fiber-seq peak and Fiber-seq reads phased for haplotype at the ZNF343 promoter (H1, n.s. as indicated; H2, p < 0.05, Fisher test).
(D) Violin plots showing the distribution of haplotype-specific FIRE score at significant (top) H1-high and (bottom) H2-high peaks. The p value comparing the score was calculated using a paired t test (p < 1.42e−50 for both).
(E) Schematic showing the calculation of nucleosome offsets for a single NDR at a TSS region. Each row represents a fiber, with the accessible patches colored red (FIRE) and purple (linker) and the nucleosomes positioned between them, in stylized fashion. The offset was computed by subtracting the center of the nucleosome at a randomly selected reference fiber from all other nucleosomes at that position relative to the location of the NDR.
(F) Boxplots showing the distribution of nucleosome offsets for the first five nucleosomes upstream and downstream TSSs with a FIRE peak. Peak-adjacent nucleosomes are colored purple, while all others are shown in gray. The p values were computed across all distributions comparing the most proximal nucleosomes to all others using Wilcoxon rank sum (p < 0.0001).
(G) Boxplots showing the distribution of nucleosome offsets for the first five nucleosomes upstream and downstream centered at randomly selected internucleosomal linker regions; linker-adjacent nucleosomes are shown in purple, while all others are shown in gray. In the randomly picked regions, no nucleosomes showed significant differences in offsets compared to the rest, via Wilcoxon rank sum.
(H) Histogram showing the absolute genomic distance between each two peaks within pairs of significant (red, N = 436, p < 0.05) and not significant (gray, N = 1,472) co-actuated pairs of peaks.
(I) Representative UCSC genome browser capture of the PLEKHG3 promoter, which is detected to have a significant co-actuation event with a nearby peak (p < 0.05).
(J) Violin plot showing the proportion of co-actuated fibers versus total fibers across all significant (red) and non-significant (gray) co-actuated pairs. Significant pairs have a median co-actuation proportion of 0.33 with an interquartile range (IQR) of 0.15. Non-significant pairs have a median co-actuation proportion of 0.18 with an IQR of 0.11.