Figure 1.
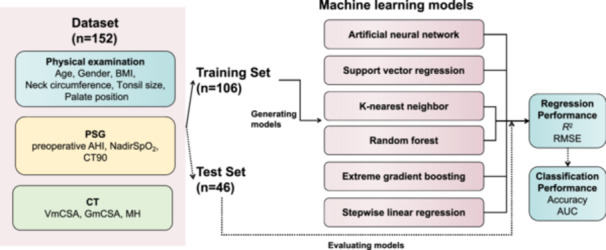
Prediction input, modeling, and evaluation. Prediction input was the parameters from physical examination, PSG, and CT. The total subjects (n = 152) were randomly divided into training and test sets by 7:3 ratio. The training set (n = 106) was used to derive the six prediction models. AHI, apnea‐hypopnea index; AUC, area under the curve; BMI, body mass index; CT, computed tomography; CT90, percentage of time with oxygen saturation below 90%; GmCSA, minimal cross‐sectional airway area of the glossopharynx; MH, the vertical distance between the lower edge of the mandible and the lower edge of the hyoid; PSG, polysomnography; RMSE, root mean square error; VmCSA, minimal cross‐sectional airway area of the velopharynx.
