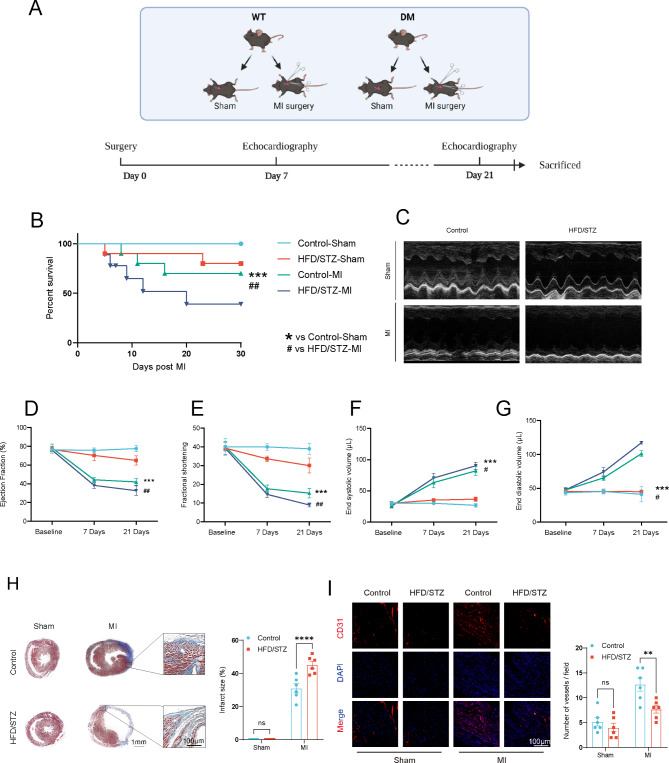
Fig. 1.
Impaired cardiac function and promoted left ventricular remodeling after permanent myocardial ischemia in HFD/STZ-induced diabetic mice. (A) a diagram of the experimental protocol. (B) Short-term survival curve after myocardial infarction and the indicated treatments (n = 10–12 mice/group). (C) Representative short-axis M-mode echocardiograms of the left ventricle in the control-Sham, HFD/STZ-Sham, control-MI, and HFD/STZ-MI groups. Left ventricular function was assessed by measurements of ejection fraction (D), LV fractional shortening (E), end diastolic volume (F), end systolic volume (G), and at day 7 and day 21 after MI (n = 6 mice/group). (H) Representative images and quantitative infarct size in Masson’s trichrome stained mice hearts on day 21 after MI (n = 6 mice/group). (I) Representative endothelial CD31 staining at the infarction border zone sections. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. Control-sham, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. Control-MI group. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments