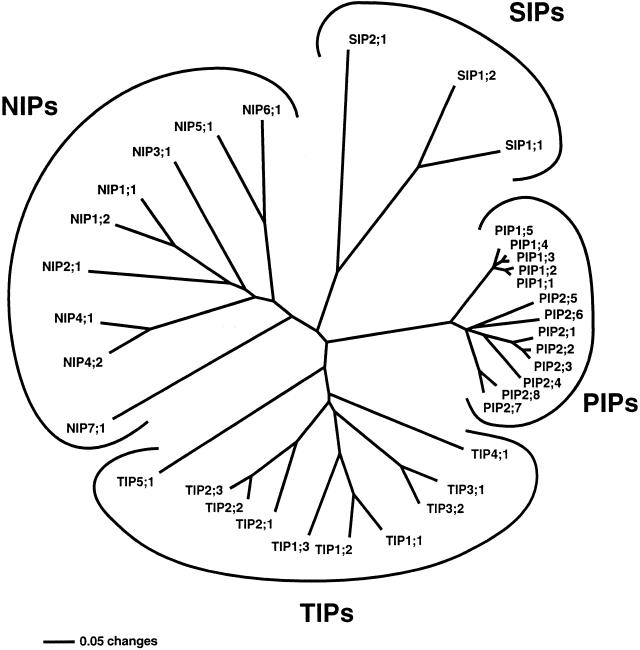
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic comparison of the complete set of 35 different MIPs encoded in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant MIPs are divided into four distinct subfamilies: PIPs, TIPs, NIPs, and SIPs. Similar proteins within a subfamily, with a maximum of 30% divergence, are clustered in monophyletic groups. The first and the last digit in the protein name identify the group and the individual gene product, respectively. This tree was obtained using the whole alignment and the distance method. Omitting the none-conserved N- and C-terminal regions from the phylogenetic analysis does not break the defined groups; only the relative positions of PIP2;6 and TIP3s is changed. In this case PIP2;6 forms a separate branch between PIP2;4 and PIP2;5 and TIP3s branch between TIP2s andTIP4;1. The bar indicates the mean distance of 0.05 changes per amino acid residue.