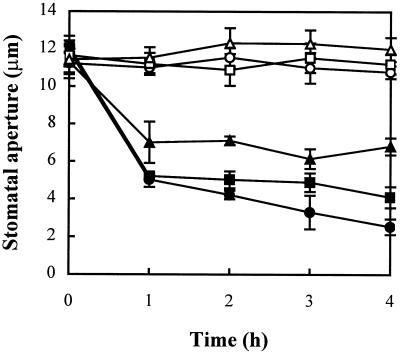
Figure 3.
Effects of ascorbic acid on the promotion of stomatal closure by H2O2. Isolated epidermis of V. faba was incubated in CO2-free MES-KCl for 3 h under conditions promoting stomatal opening and then transferred to fresh CO2-free MES-KCl containing no (○), 10−5 m H2O2 (●), 10−5 m H2O2 + 1 mm ascorbic acid (▪), 10−5 m H2O2 + 10 mm ascorbic acid (▴), 1 mm (□), or 10 mm (Δ) ascorbic acid only for another 4 h. Stomatal apertures were determined at 1-h intervals during the 4-h incubation. Values are the means of 120 measurements ± se.