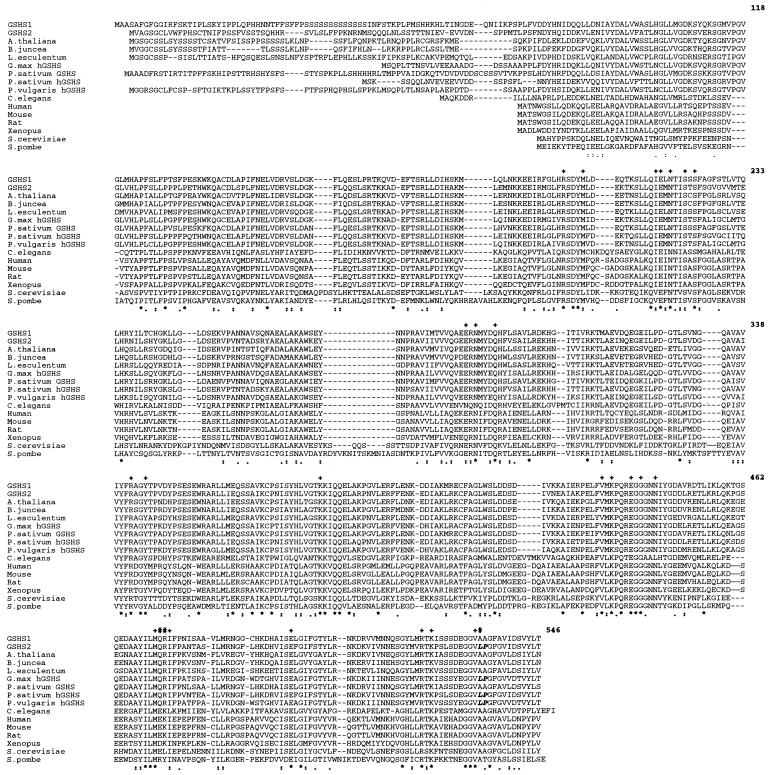
Figure 1.
Multiple alignment of eukaryotic GSHS and hGSHS. SWISSPROT-TREMBL accession nos. are as follows: Q21549 (M176.2, Caenorhabditis elegans), P46413 (GSHS rat [Rattus norvegicus]), P51855 (GSHS mouse [Mus musculus]), P48637 (GSHS human), P35668 (GSHS African clawed frog [Xenopus laevis]), Q08220 (GSHS baker's yeast [Saccharomyces cerevisiae]), P35669 (GSHS fission yeast [Schizosaccharomyces pombe]), O22494 (GSHS tomato [Lycopersicon esculentum]), O23732 (GSHS leaf mustard [Brassica juncea]), AJ243812 (GSHS Arabidopsis), AJ272035 (hGSHS G. max), AF194421 (GSHS1 M. truncatula), AF194422 (GSHS2 M. truncatula), AF258320 (hGSHS P. vulgaris), AF258319 (hGSHS P. sativum), and AF231137 (GSHS P. sativum). Amino acid residues corresponding to GSHS2 are numbered on the right. Stars represent identical amino acids and dots represent conserved amino acids (below). Amino acids involved in the catalytic site of human GSHS and conserved in GSHS2 are represented by + and amino acids located in the catalytic site of human GSHS and changed in GSHS2 are represented by # (above). Leu534 and Pro535 are represented in bold letters.