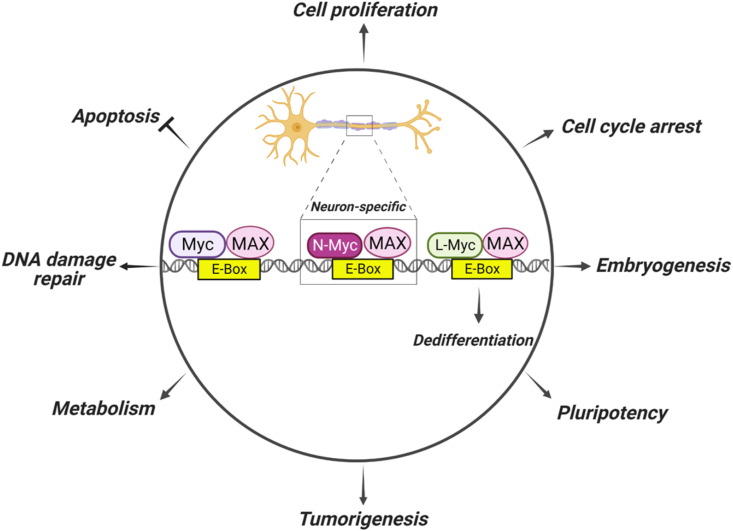
Figure 1.
Oncogenic transcriptional regulation of the MYC family. The Myc family of transcription factors, including Myc, N-Myc, and L-Myc, bind DNA at specific sequences and regulate gene expression by binding to enhancer-box (E-Box) sequences via dimerization with Myc-associated factor X (MAX). Downstream gene expression contributes to oncogenic functions by promoting proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis, stimulating pluripotency, promoting embryogenesis, leading to abnormal metabolic regulation, increasing DNA damage repair to bypass cell death, and reducing differentiation, all of which result in more aggressive tumor growth and/or a drug-resistant phenotype.