Figure 3.
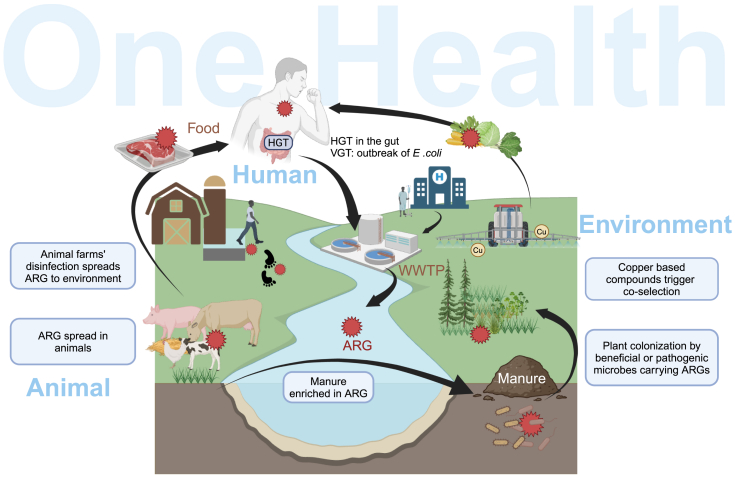
ARGs in One Health - dissemination and selection across environments and reservoirs
Humans, animals, and the environment are intertwined components of One Health, contributing to the spread of antimicrobial resistance through different routes. For instance, the use of antibiotics in clinical settings and animal husbandry contributes to the selection of ARGs that further spread via waterways and in WWTPs. Likewise, the use of biocides, such as copper and disinfectants, in agriculture and animal husbandry might contribute to the co-selection of ARGs. The use of wastewater for irrigation, or ARG-enriched manure, can further promote the spread of ARGs in soils and crops. Finally, residues of antimicrobials or other biocides in food products can lead to stronger selective pressure in the human gut, promoting the spread of ARGs via clonal expansion (VGT) or through HGT.