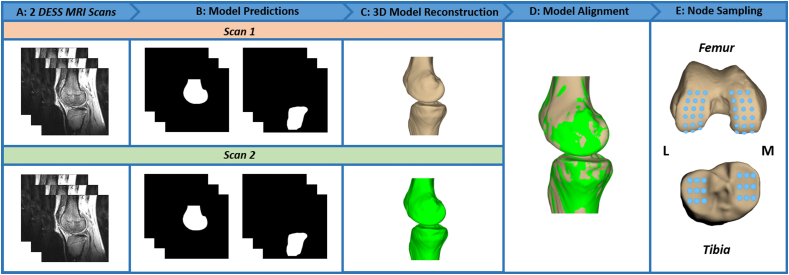
Fig. 1.
Bone Surface DistanceRepeatability Analysis Pipeline. (A) To assess bone surface repeatability, two DESS MRI scans from a single participant are inputted into the trained tibia and femur segmentation models. (B) The trained models predict the tibia and femur masks. (C) The outer contours from the predicted masks are extracted and reconstructed into 3D models using Geomagic Studio 11 (3D Systems; Research Triangle Park, North Carolina). (D) The tibia and femur models from Scan 1 and Scan 2 are aligned using an iterative closest point technique [6]. (E) Bone surface distances in the x-, y-, and z-directions are calculated between the two scans across all regions of interest [28]. M = medial and L = lateral.