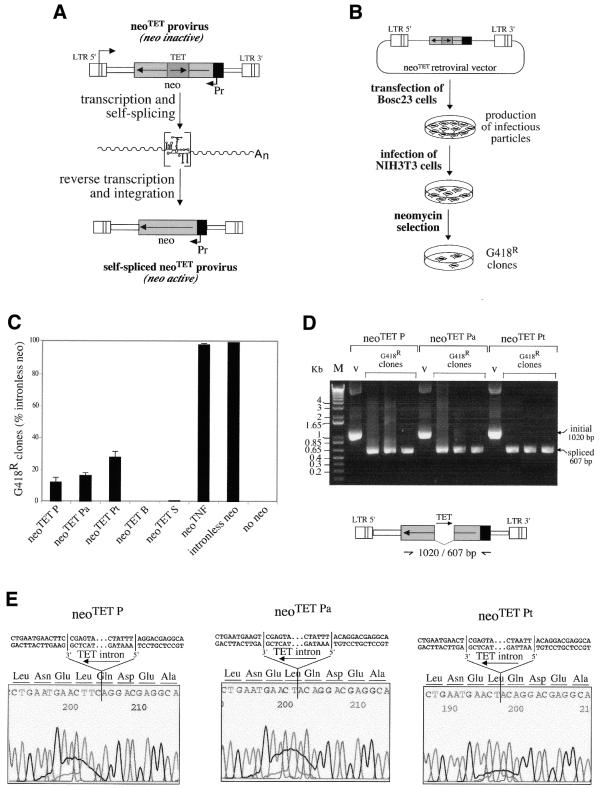
Figure 4.
Quantitative assay for the splicing of the modified Tetrahymena introns and for the neoTET cassettes. (A) Rationale of the assay: in the initial copy of the neoTET marked gene, the neomycin gene-coding sequence (neo) is interrupted by the Tetrahymena intron, and cells containing the marked gene should be G418-sensitive. Upon transcription of the marked gene, the Tetrahymena intron should be spliced out and, after reverse transcription and integration (i.e. retrotransposition), the neo gene in the transposed copy should be active and the cells be G418-resistant. (B) Experimental procedures for the assay of the neoTET cassette. The neoTET cassette was introduced into a Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived vector, as illustrated. The corresponding plasmids were then introduced by transfection into a viral packaging cell line (Bosc23); the supernatants of the transfected packaging cells were collected, and used to infect target NIH3T3 cells. The 3T3 cells were then submitted to G418 selection to quantify the number of G418-resistant cells. DNAs from the resulting clones were finally extracted and analyzed (D and E) for the precise splicing out of the Tetrahymena intron. (C) Splicing and reporter gene efficiency as measured by the number of G418-resistant clones after retroviral transduction of the neo-containing cassettes. G418 selections were performed on plates seeded with 5 × 104 cells (NIH3T3) per plate, and infected with 1 ml of transfected Bosc23 supernatant. The number of foci per plate is indicated for the five modified Tetrahymena intron-containing cassettes, the TNF intron-containing cassette, a positive control with an intronless neo cassette taken as a reference (100%) and a negative control without the neo gene; bars indicate standard deviations. (D) DNAs from individual clones were assayed by PCR for the presence of spliced copies, using primers bracketting the intronic domain. Positions of the primers used and sizes of the expected bands are indicated in the schema below the BET-labeled agarose gel. Bands of the expected size for the spliced-out intron (607 bp) are observed for all tested G418R clones, with a larger band (1020 bp) in the three control lanes (v, vector DNA). (E) Sequencing of the junctions of the spliced Tetrahymena introns. PCR products in (D) were sequenced, disclosing precise splicing out of the modified P, Pa and Pt Tetrahymena introns which restores the phase of the neo-coding sequence.