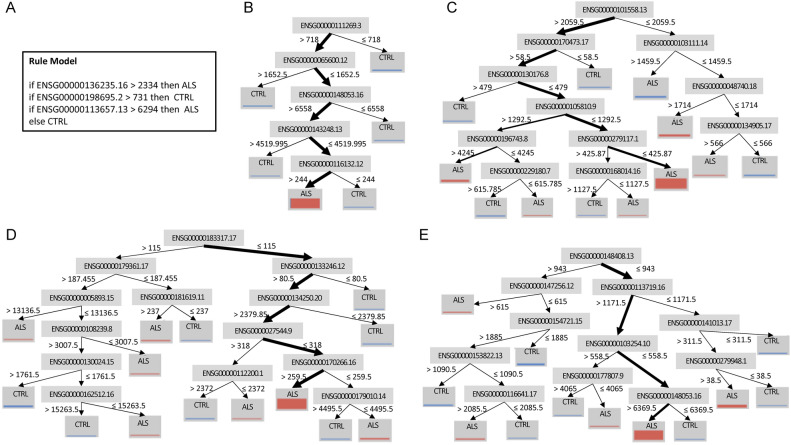
Fig. 4.
The binary classifiers of ALS. (A) Rule induction. Rule induction systematically identifies patterns in the data and constructs a set of "if–then" rules that can be used to make predictions. For ALS classification, the rule induction classifier determines a series of logical conditions that differentiate ALS samples from control samples based on gene expression patterns. (B) Decision tree. The decision tree classifier uses the gene expression data to form a tree-like structure where each node represents a decision about a specific gene. The branches of the tree lead to different classifications—either ALS or control—based on the outcomes of these decisions. (C–E) Decision trees from Random forest. Each individual decision tree in a Random Forest is constructed from a random subset of the data, and the final classification is determined by aggregating the predictions from all the trees. In (B–E), the judgment criteria are noted near the splitting arrows, and the thickness of the arrows roughly represents the fraction of samples that fall in this criterion.