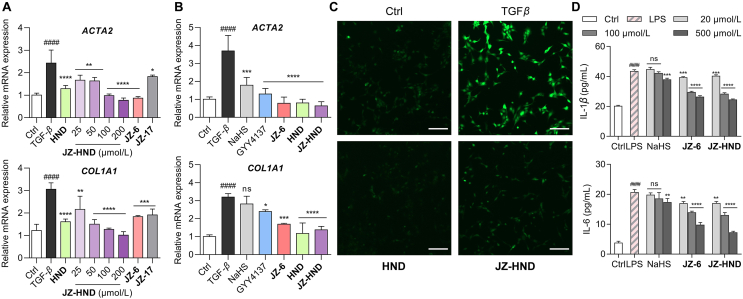
Figure 5.
JZ-HND and JZ-6 combined multiple protections at the cellular level, including antifibrosis, antioxidation, and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion. (A, B) JZ-HND attenuated TGFβ1-induced cellular fibrosis through the synergistic effect of H2S with HND. Relative ACTA2 and COL1A1 mRNA expression in LX-2 cells. Gene expression was normalized to ACTB mRNA levels. LX-2 cells were incubated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) and HND (200 μmol/L), JZ-HND (25, 50, 100, and 200 μmol/L), JZ-6 (200 μmol/L), JZ-10 (200 μmol/L), NaHS (200 μmol/L), or GYY4137 (200 μmol/L) for 72 h. (C) Reduction of ROS levels induced by TGF-β1 in LX-2 cells. Cells were treated with TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL) and HND (100 μmol/L) or JZ-HND (100 μmol/L) for 24 h, then ROS were detected by fluorescence imaging using DCFH-DA (10 μmol/L); Scale bars = 200 μm. (D) Effects on LPS-induced IL-1β and IL-6 release in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of NaHS, JZ-6, or JZ-HND for 1 h prior to incubation with LPS (1 μg/mL). After incubation for 24 h, the levels of IL-1β and IL-6 present in the supernatants were measured using ELISA kits. Data represent mean ± SD of independent experiments (n = 3). ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗P < 0.05 versus model group and ####P < 0.0001 versus control group. ns, not significant.