Abstract
The effect of hyperphenylalaninaemia on the metabolism of ketone bodies in vivo and in vitro by developing rat brain was investigated. The incorporation in vivo of [14C]acetoacetate into cerebral lipids was decreased by both chronic (for 3 days) and acute (for 6h) hyperphenylalaninaemia induced by injecting phenylalanine into 1-week-old rats. In studies in vitro it was observed that the incorporation of the radioactivity from [14C]acetoacetate and 3-hydroxy[14C]butyrate into cerebral lipids was inhibited by phenyl-pyruvate, but not by phenylalanine. Phenylpyruvate also inhibited the incorporation of 3H from 3H2O into lipids by brain slices metabolizing either 3-hydroxybutyrate or acetoacetate in the presence of glucose. These findings suggest that the decrease in the incorporation in vivo of [14C]acetoacetate into cerebral lipids in hyperphenylalaninaemic rats is most likely caused by phenylpyruvate and not by phenylalanine. Phenylpyruvate as well as phenylalanine had no inhibitory effects on ketone-body-catabolizing enzymes, namely 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, 3-oxo acid CoA-transferase and acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase, in rat brain. Phenylpyruvate but not phenylalanine inhibited the activity of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex from rat and human brain. These findings suggest that the metabolism of ketone bodies is impaired in brains of untreated phenylketonuric patients, and in turn may contribute to the diminution of mental development and function associated with phenylketonuria.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal H. C., Bone A. H., Davison A. N. Effect of phenylalanine on protein synthesis in the developing rat brain. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):325–331. doi: 10.1042/bj1170325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anson R. W., Ballard F. J. The metabolic fate of the products of citrate cleavage. Adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked malate dehydrogenase in foetal and adult liver from ruminants and non-ruminants. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):705–713. doi: 10.1042/bj1080705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbato L., Barbato I. W., Hamanaka A. The in vivo effect of high levels of phenylalanine on lipids and RNA of the developing rabbit brain. Brain Res. 1968 Mar;7(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl S., Nicklas W. J., Clarke D. D. Compartmentation of glutamic acid metabolism in brain slices. J Neurochem. 1968 Feb;15(2):131–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROME L., TYMMS V., WOOLF L. I. A chemical investigation of the defects of myelination in phenylketonuria. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 May;25:143–148. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. P., O'Brien D. Effect of excess phenylalanine and of other amino acids on brain development in the infant rat. Pediatr Res. 1970 Jan;4(1):96–102. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197001000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. B., Nicklas W. J. The metabolism of rat brain mitochondria. Preparation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4724–4731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Lowden J. A. Hyperphenylalaninemia: effect on the developing rat brain. Can J Biochem. 1969 Mar;47(3):291–295. doi: 10.1139/o69-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmond J. Ketone bodies as precursors of sterols and fatty acids in the developing rat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatt J. P., Ball E. G. Studies on the metabolism of adipose tissue. XIX. An evaluation of the major pathways of glucose catabolism as influenced by acetate in the presence of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 25;241(12):2862–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. W., Katz J. The distribution of tritium in fatty acids synthesized from tritiated glucose and tritiated water by rat adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Brand M. D., Denton R. M. Inhibition of mitochondrial pyruvate transport by phenylpyruvate and alpha-ketoisocaproate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 10;367(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Williamson D. H., Krebs H. A. Ketone-body utilization by adult and suckling rat brain in vivo. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):13–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1220013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Shah S. N. Effect of hyperphenylalaninemia on fatty acid composition of lipids of rat brain myelin. J Neurochem. 1973 Nov;21(5):1225–1240. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungas R. L. Fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue incubated in tritiated water. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3708–3717. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Hems R., Weidemann M. J., Speake R. N. The fate of isotopic carbon in kidney cortex synthesizing glucose from lactate. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):242–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1010242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land J. M., Clark J. B. Effect of phenylpyruvate on enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis in rat brain. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):545–555. doi: 10.1042/bj1340545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land J. M., Clark J. B. Inhibition of pyruvate and beta-hydroxybutyrate oxidation in rat brain mitochondria by phenylpyruvate and alpha-ketoisocaproate. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):348–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., BUNKER W. E. Preparation of tissue slices for metabolic studies: a hand-microtome especially suitable for brain. J Neurochem. 1957;2(1):11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. H., Aeberhard E. Maternal phenylketonuria. The composition of cerebral lipids in an affected offspring. J Pediatr. 1969 Jun;74(6):924–931. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. H. Cerebral proteolipids in phenylketonuria. Neurology. 1968 Oct;18(10):1003–1008. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.10.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. L., Hawkins R. A., Veech R. L. Phenylketonuria: phenylalanine inhibits brain pyruvate kinase in vivo. Science. 1973 Mar 2;179(4076):904–906. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4076.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Reichard G. A., Jr, Markus H., Boden G., Mozzoli M. A., Shuman C. R. Rapid intravenous sodium acetoacetate infusion in man. Metabolic and kinetic responses. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2606–2616. doi: 10.1172/JCI107453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. A., Krebs H. A., Williamson D. H. Activities of enzymes of ketone-body utilization in brain and other tissues of suckling rats. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(1):49–53. doi: 10.1042/bj1210049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S., Arinze I. J. Phenylketonuria: metabolic alterations induced by phenylalanine and phenylpyruvate. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975 Feb;28(2):183–188. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/28.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S., Grover W. D., Auerbach V. H. Pyruvate metabolism by homogenates of human brain: effects of phenylpyruvate and implications for the etiology of the mental retardation in phenylketonuria. J Neurochem. 1973 Feb;20(2):289–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
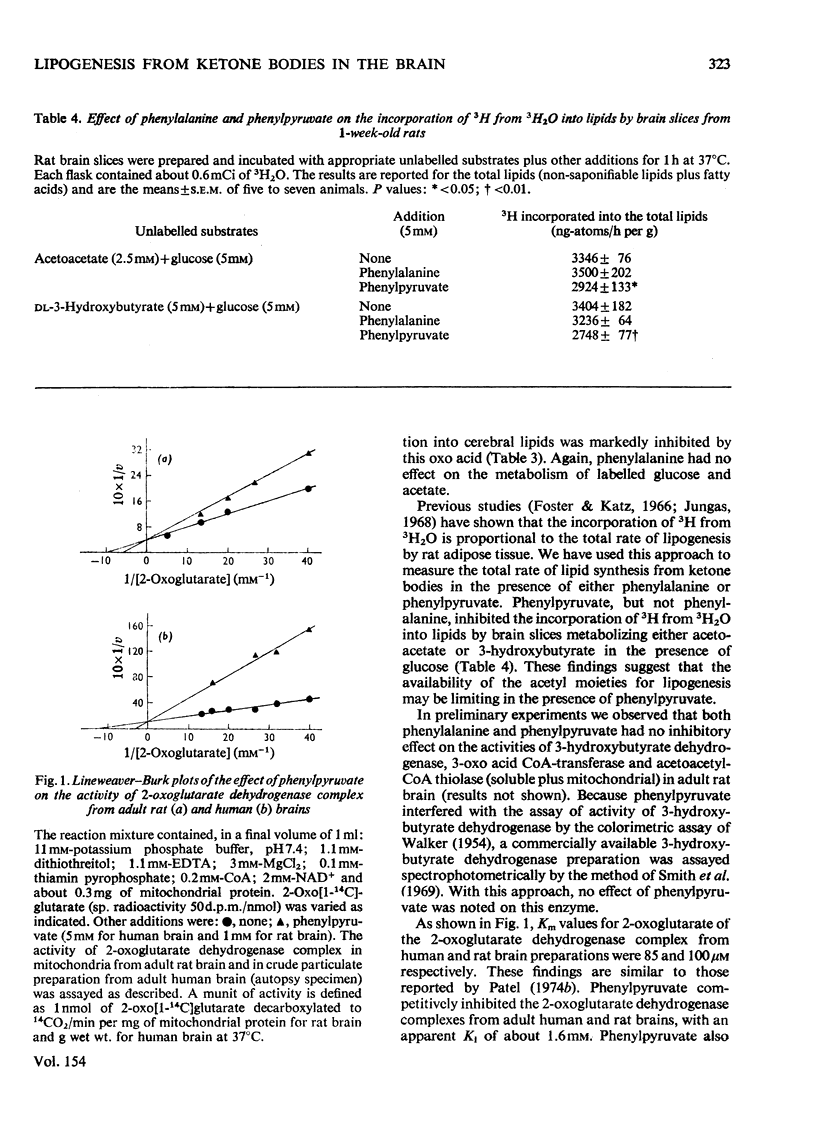
- Patel M. S. Inhibition by the branched-chain 2-oxo acids of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in developing rat and human brain. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):91–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1440091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S. The effect of phenylpyruvate on pyruvate metabolism in rat brain. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):677–684. doi: 10.1042/bj1280677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S. The relative significance of CO2-fixing enzymes in the metabolism of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1974 May;22(5):717–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. N., Peterson N. A., McKean C. M. Cerebral lipid metabolism in experimental hyperphenylalaninaemia: incorporation of 14C-labelled glucose into total lipids. J Neurochem. 1970 Feb;17(2):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. N., Peterson N. A., McKean C. M. Impaired myelin formation in experimental hyperphenylalaninaemia. J Neurochem. 1972 Feb;19(2):479–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. N., Peterson N. A., McKean C. M. Inhibition of in vitro sterol biosynthesis by phenylalanine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 18;164(3):604–606. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. N., Peterson N. A., McKean C. M. Inhibition of sterol synthesis in vitro by metabolites of phenylalanine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;187(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Satterthwaite H. S., Sokoloff L. Induction of brain D(--)-beta-hydroxybytrate dehydrogenase activity by fasting. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):79–81. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaiman K. F., Hosfield W. B., Lemieux B. Elevated plasma phenylalanine concentration and lysine incorporation into ribosomal protein of developing brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Jul;15(7):687–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER P. G. A colorimetric method for the estimation of acetoacetate. Biochem J. 1954 Dec;58(4):699–704. doi: 10.1042/bj0580699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Glazer R. I., Ross R. A. Regulation of human and rat brain metabolism: inhibitory action of phenylalanine and phenylpyruvate on glycolysis, protein, lipid, DNA, and RNA metabolism. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;8:13–36. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(70)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Bates M. W., Page M. A., Krebs H. A. Activities of enzymes involved in acetoacetate utilization in adult mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(1):41–47. doi: 10.1042/bj1210041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


