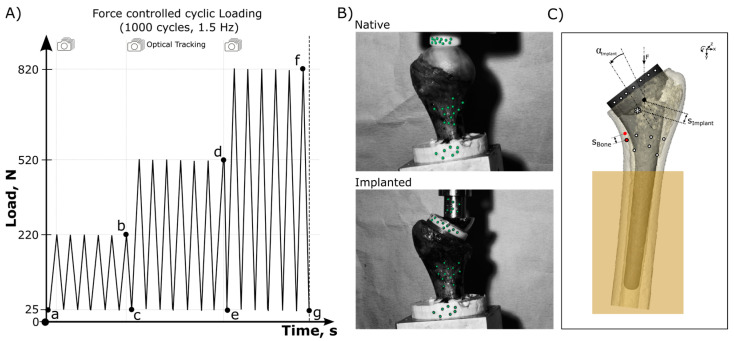
Figure 4.
(A) Testing protocol shows the loading cycles including the points of data analysis (a–g). (B) Experimental cyclic loading setups and the optical tracking points (green) for data analysis. (C) Evaluated tracking points during cyclic loading force (F) to analyze implant subsidence and tilt measurements between analysis points a and b, d or f, respectively, (simlant and αimlant, Δab, Δad, and Δaf) at the end of each loading block. Bone micromotion (sBoneHW, Δbc, Δde, and Δfg) was evaluated as bone displacement within each final load cycle (hysteresis width (HW)). Total compressive transmission caused deformation of the bone was measured at the end of each loading block (sBoneTot, Δab, Δad, and Δaf).