Abstract
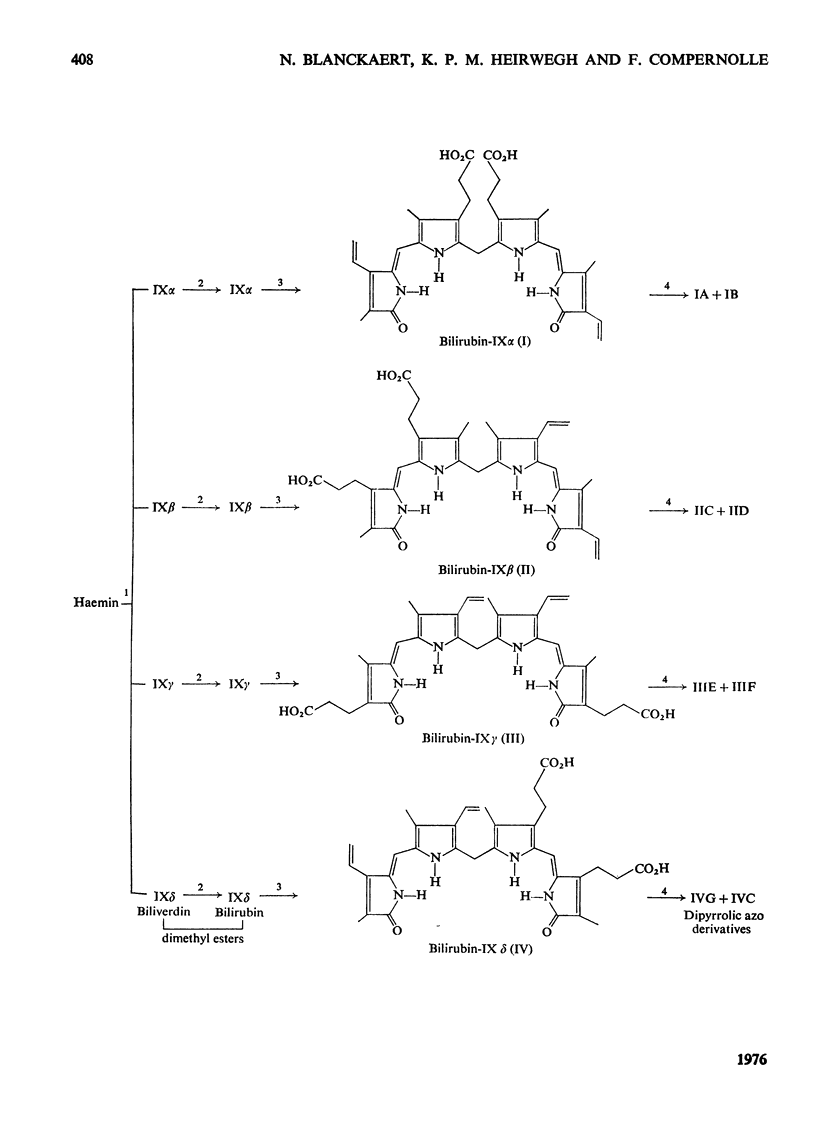
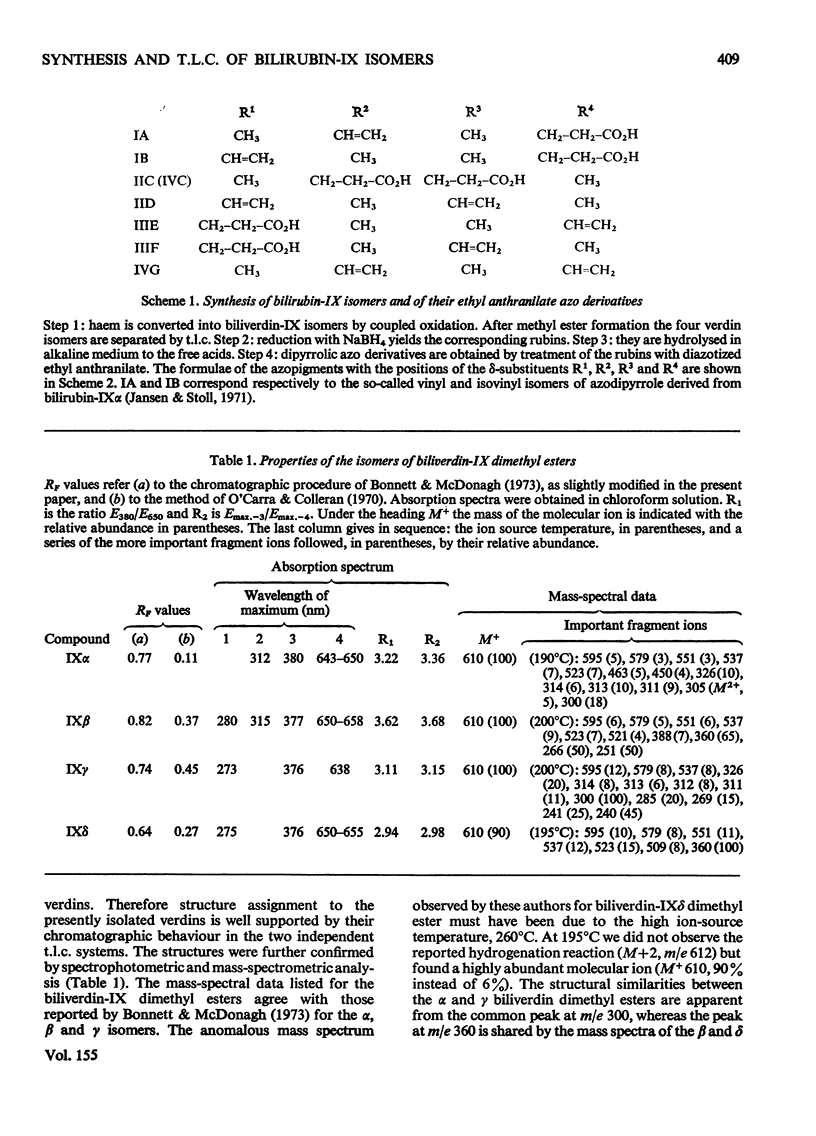
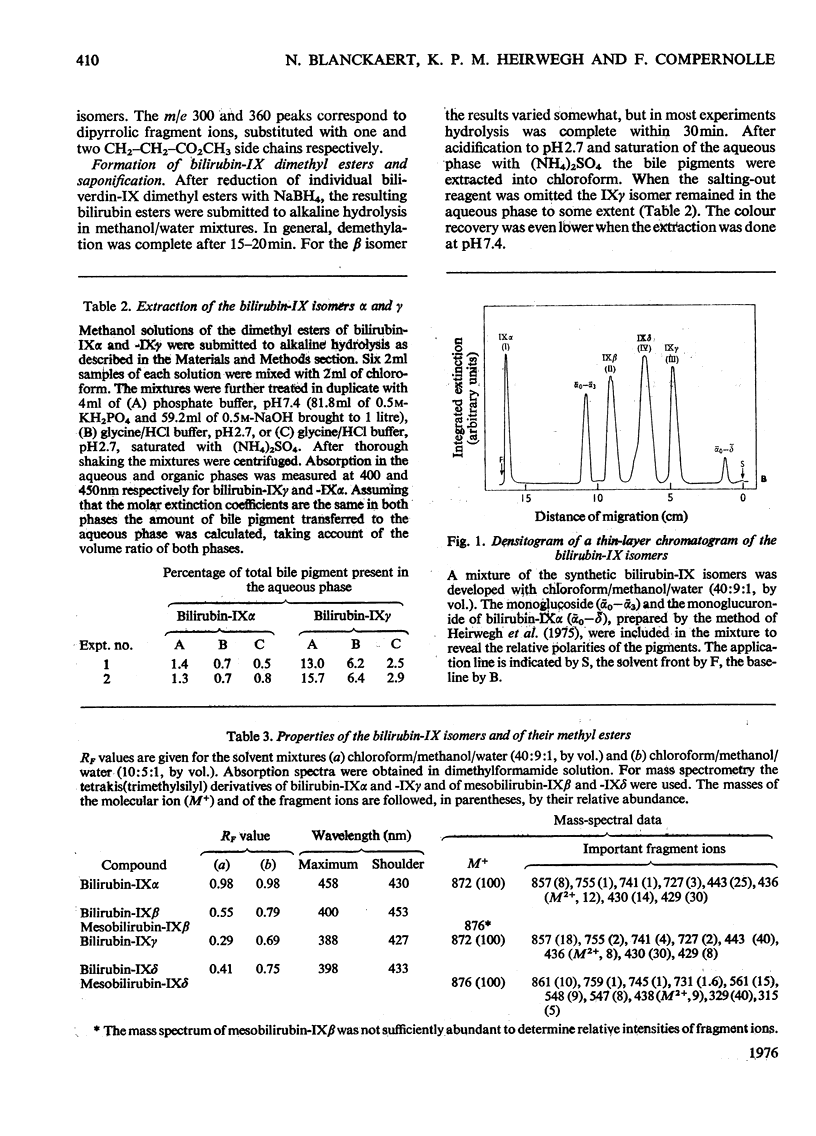
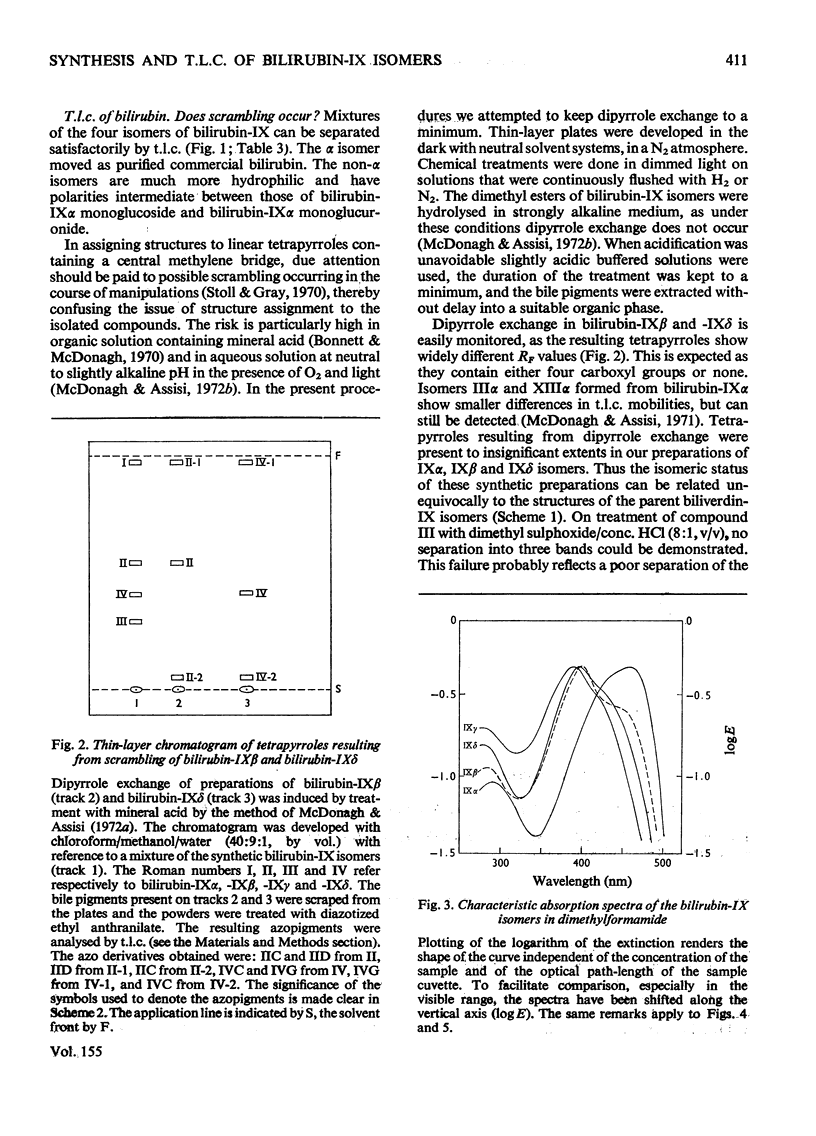
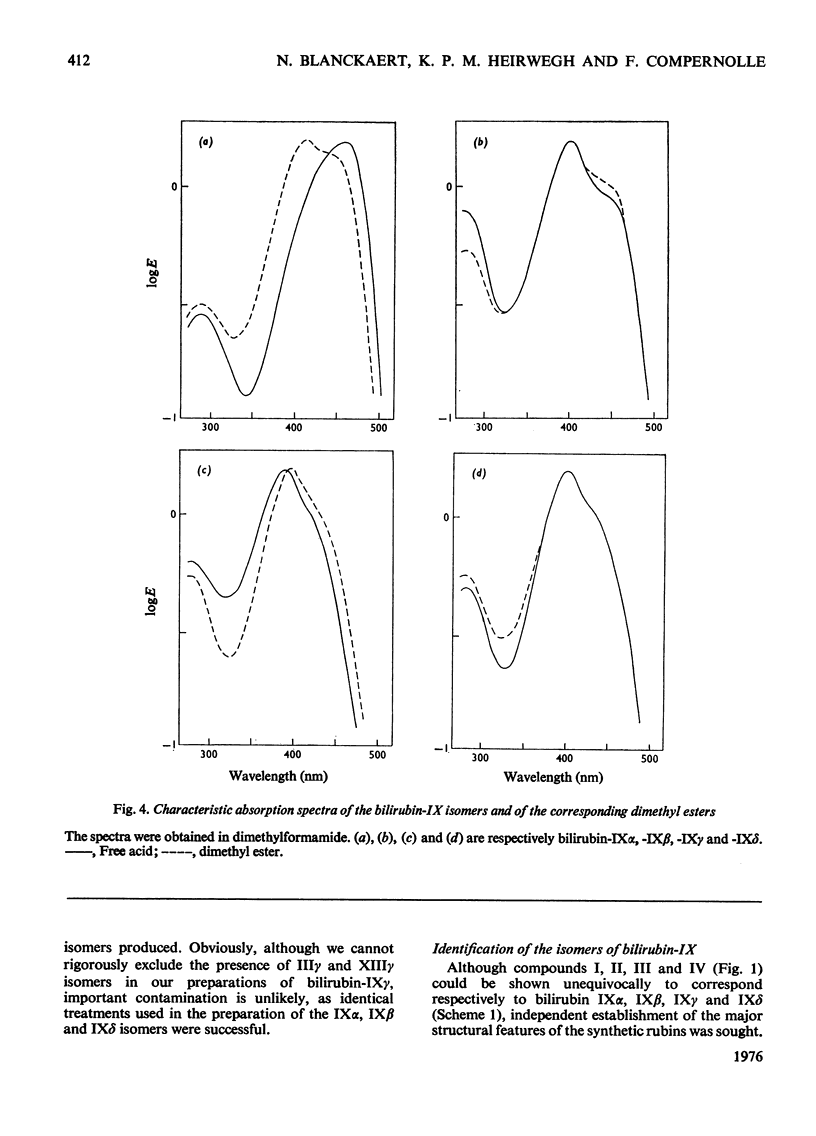
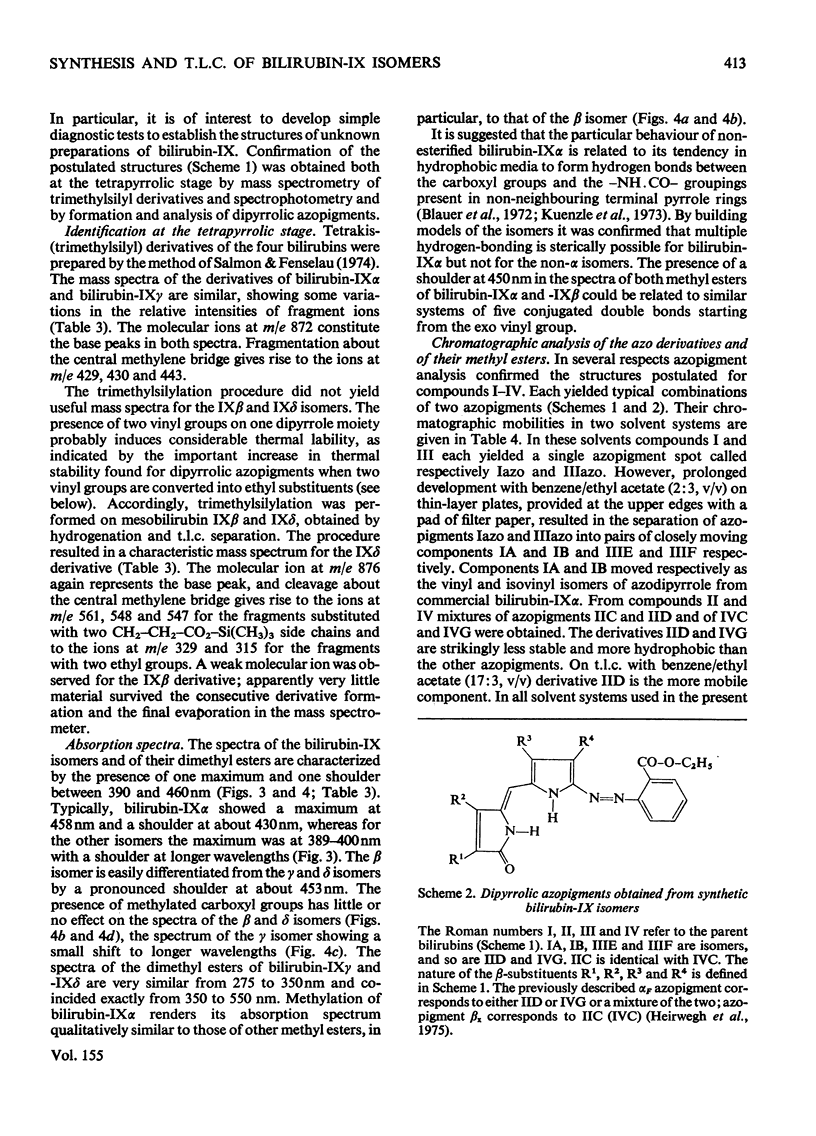
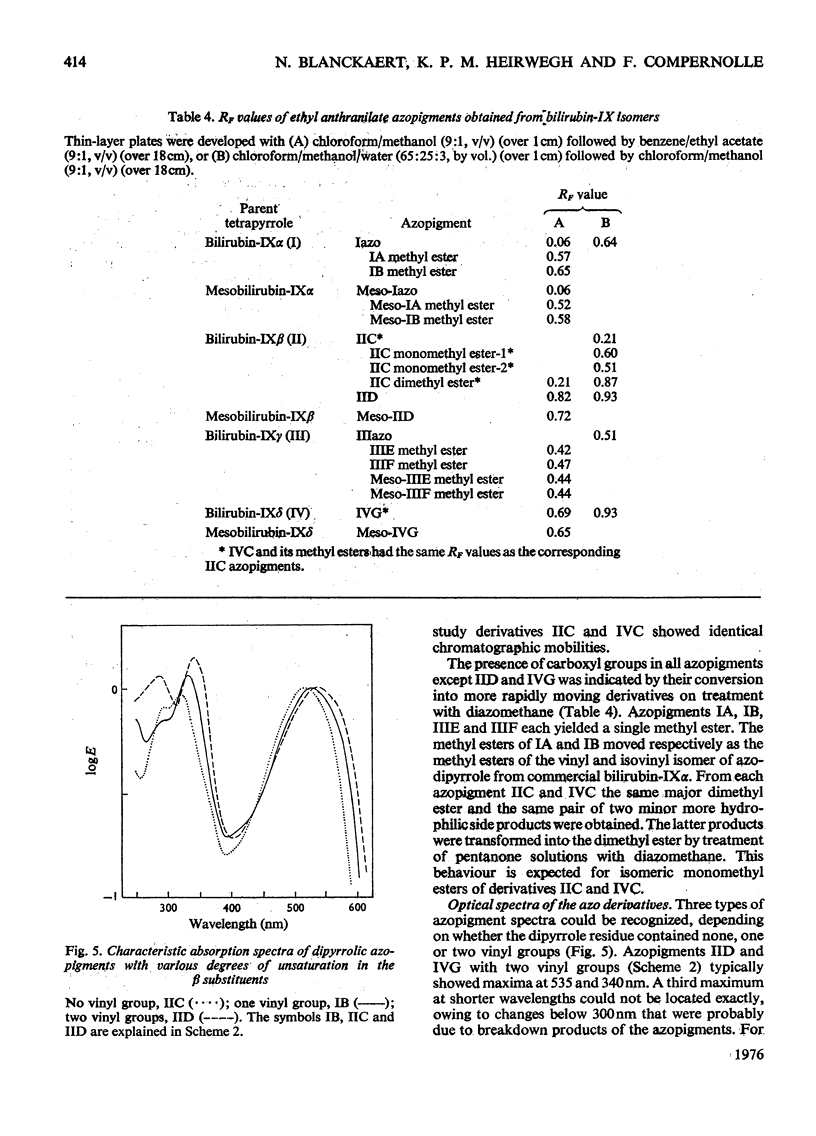
Procedures for the synthesis, separation and determination of structure of the bilirubin-IX isomers are described. 1. The four biliverdin-IX isomers were prepared by oxidative cleavage of haemin and were separated as their dimethyl esters. The individual esters were reduced with NaBH4, and the bilirubin esters obtained were subjected to alkaline hydrolysis yielding the corresponding bilirubin-IX isomers. 2. The bilirubin-IX isomers were structurally characterized (a) at the tetrapyrrolic stage by mass spectrometry of their trimethylsilyl derivatives and (b) by formation and structural analysis of their dipyrrolic ethyl anthranilate azo derivatives. 3. The absorption spectrum of bilirubin-IX alpha differed strikingly from the spectra of the other isomers. The presence of a pronounced shoulder around 453 nm in the spectrum of bilirubin-IXbeta allows easy differentiation from bilirubin-IXdelta. Methylation of the carboxyl groups largely eliminates the spectral differences between the IXalpha- and non-alpha isomers. 4. The bilirubin-IX isomers are conveniently separated by t.l.c. Detection and unequivocal identification is possible on a micro-scale by (a) t.l.c. with respect to reference compounds and (b) subsequent formation and t.l.c. of the more stable ethyl anthranilate azopigments. 5. Pronounced differences in polarity, i.e. solvent distribution, between the bilirubin-IX isomers indicate that a re-evaluation of conclusions reached previously with regard to the presence in, or absence from, biological fluids of some isomers and their relative amounts is needed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODERSEN R., VIND I. Chloroform extraction of serum bilirubin in relation to its binding to proteins. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blauer G., Harmatz D., Snir J. Optical properties of bilirubin-serum albumin complexes in aqueous solution. I. Dependence on pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):68–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnett R., McDonagh A. F. The meso-reactivity of porphyrins and related compounds. VI. Oxidative cleavage of the haem system. The four isomeric biliverdins of the IX series. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1973;9:881–888. doi: 10.1039/p19730000881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D., Winsnes A. Determination of conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin by methods based on direct spectrophotometry and chloroform-extraction. A reappraisal. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;28(1):41–48. doi: 10.3109/00365517109090661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compernolle F., Van Hees G. P., Fevery J., Heirwegh K. P. Mass-spectrometric structure elucidation of dog bile azopigments as the acyl glycosides of glucopyranose and xylopyranose. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):811–819. doi: 10.1042/bj1250811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. H., Nicholson D. C., Tipton G. Degradation of haem compounds to bile pigments. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 6;239(88):5–8. doi: 10.1038/newbio239005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heirwegh K. P., Fevery J., Michiels R., van Hees G. P., Compernolle F. Separation by thin-layer chromatography and structure elucidation of bilirubin conjugates isolated from dog bile. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):185–199. doi: 10.1042/bj1450185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen F. H., Stoll M. S. Separation and structural analysis of vinyl- and isovinyl-azobilirubin derivatives. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):585–597. doi: 10.1042/bj1250585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C., Weibel M. H., Pelloni R. R., Hemmerich P. Structure and conformation of bilirubin. Opposing views that invoke tautomeric equilibria, hydrogen bonding and a betaine may be reconciled by a single resonance hybrid. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):364–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1330364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. Commercial bilirubin: A trinity of isomers. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):315–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80475-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. The ready isomerization of bilirubin IX- in aqueous solution. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1290797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carra P., Colleran E. Separation and identification of biliverdin isomers and isomer analysis of phycobilins and bilirubin. J Chromatogr. 1970 Aug 12;50(3):458–468. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETRYKA Z., NICHOLSON D. C., GRAY C. H. Isomeric bile pigments as products of the in vitro fission of haemin. Nature. 1962 Jun 16;194:1047–1048. doi: 10.1038/1941047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdiger W. Chromsäure- und Chromatabbau con Gallengarbstoffen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Nov;350(11):1291–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon M., Fenselau C. Evaluation of bilirubin derivatives for mass spectral analysis. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1974 Aug;1(4):219–222. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Gray C. H. The oxidation products of crude mesobilirubinogen. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):271–290. doi: 10.1042/bj1170271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipton G., Gray C. H. Gas chromatographic analysis of pyrrolic acid esters from the potassium permanganate oxidation of bile pigments. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):29–43. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F. P., Heirwegh K. P. Determination of bilirubin glucuronide and assay of glucuronyltransferase with bilirubin as acceptor. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):507–518. doi: 10.1042/bj1070507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


