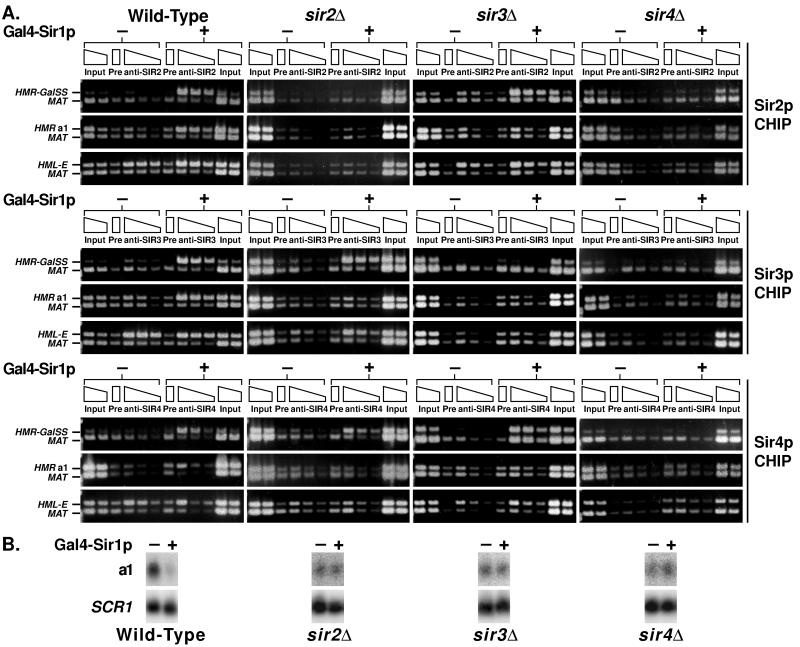
Figure 6.
Loading and spreading of Sir proteins at a synthetic silencer. (A) Chromatin immunoprecipitations from SIR, sir2Δ, sir3Δ, or sir4Δ strains (left-to-right columns; JRY7131, JRY7303, JRY7304, and JRY7305, respectively). Cells contained 4xGal4-RAP1-ABF1 HMRa ΔI at HMR, and Gal4-Sir1p was repressed (−, first six lanes) or expressed (+, second six lanes). Wild-type Sir1p was constitutively expressed and acted at HML but not the synthetic silencer at HMR. DNA immunoprecipitated with antibodies against Sir2p (top), Sir3p (middle), or Sir4p (bottom) was analyzed by simultaneous amplification of the synthetic silencer (top band, top gels), the a1 open reading frame (top band, middle gels), or HML-E (top band, bottom gels) and sequences adjacent to MAT (bottom band, all gels). Negative controls (lanes Pre) had samples immunoprecipitated with rabbit sera from unimmunized rabbits. 1/7500, 1/15,000, or 1/30,000 of the input DNA or 1/100, 1/200, or 1/400 of the immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed. In this experiment, the ratio of immunoprecipitated HMR to MAT DNA was smaller than the ratio of immunoprecipitated HMR to SSC1 DNA in previous experiments. Consequently, these images reflect longer exposures than those in other figures, and the negative control is more visible. (B) RNA was isolated from the same samples used in part A in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of Gal4-Sir1p and analyzed for a1 or SCR1 mRNA.