Figure 4.
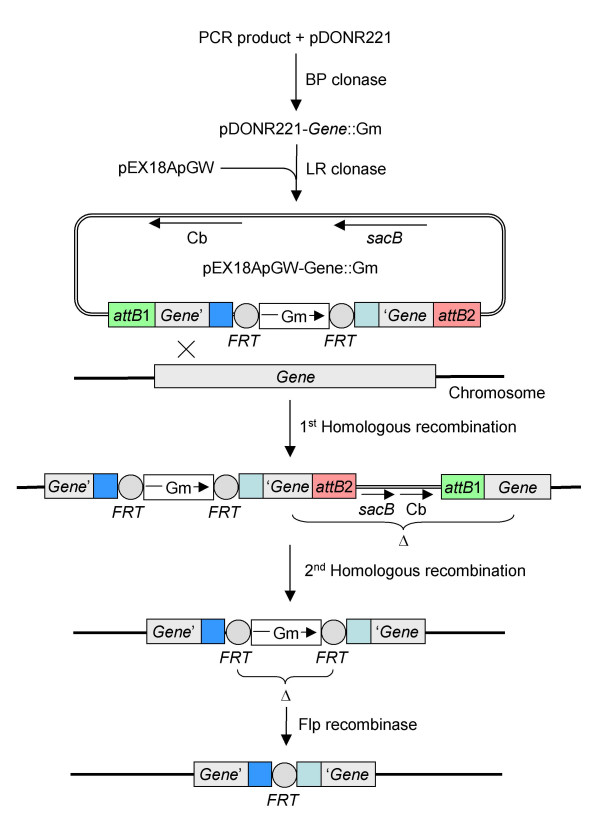
Gateway-recombinational cloning and return of the plasmid-borne deletion allele to the P. aeruginosa chromosome. The mutant DNA fragment generated by overlap extension PCR is first cloned into pDONR221 via the BP clonase reaction to create the entry clone pDONR221-Gene::Gm, which then serves as the substrate for LR clonase-mediated recombination into the destination vector pEX18ApGW. The resulting suicide vector pEX18ApGW-Gene::Gm is then transferred to P. aeruginosa and the plasmid-borne deletion mutation is exchanged with the chromosome to generate the desired deletion mutant. Please note that, as discussed in the text, gene replacement by double-crossover can occur quite frequently, but it can also be a rare event in which case allele exchange happens in two steps involving homologous recombination. First, the suicide plasmid is integrated via a single-crossover event resulting in generation of a merodiploid containing the wild-type and mutant allele. Second, the merodiploid state is resolved by sacB-mediated sucrose counterselection in the presence of gentamycin, resulting in generation of the illustrated chromosomal deletion mutant. An unmarked mutant is then obtained after Flp recombinase-mediated excision of the Gm marker.
