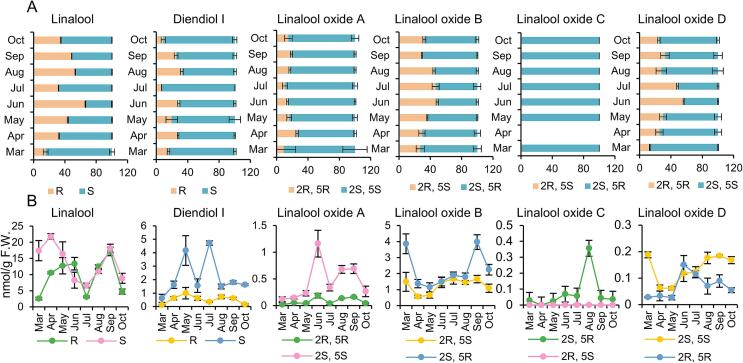
Fig. 3.
Seasonal variation of linalool and its derivatives in one bud and two leaves of cultivated ‘Hainan dayezhong’ tea tree.
A, dynamics of chiral isomer ratio. Statistically significant difference between months was analyzed by One-way ANOVA. linalool: F = 517.367, P < 0.001; diendiol I: F = 29.209, P < 0.001; linalool oxide A: F = 2.361, P = 0.073; linalool oxide B: F = 25.802, P < 0.001; linalool oxide D: F = 15.282, P < 0.001. B, dynamics of chiral isomer content. Statistically significant difference between months was analyzed by One-way ANOVA. S-linalool: F = 8.525, P < 0.001; R-linalool: F = 18.568, P < 0.001; S-diendiol I: F = 25.592, P < 0.001; R-diendiol I: F = 8.569, P < 0.001; (2S, 5S)-linalool oxide A: F = 32.921, P < 0.001; (2R, 5R)-linalool oxide A: F = 26.999, P < 0.001; (2S, 5R)-linalool oxide B: F = 27.932, P < 0.001; (2R, 5S)-linalool oxide B: F = 6.242, P < 0.001; (2S, 5R)-linalool oxide C: F = 571.696, P < 0.001; (2R, 5S)-linalool oxide C: F = 101.812, P < 0.001; (2S, 5S)-linalool oxide D: F = 145.164, P < 0.001; (2R, 5R)-linalool oxide D: F = 14.223, P < 0.001. All the statistical analysis were performed using SPSS 29.