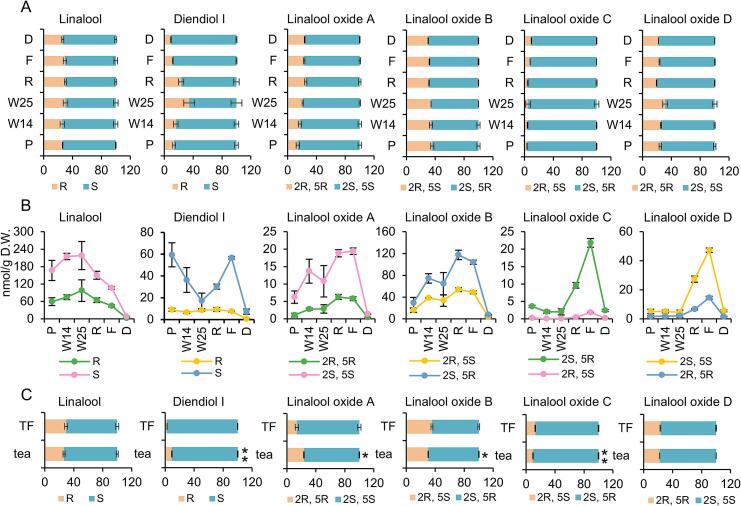
Fig. 6.
Dynamic change of chiral configuration of linalool and its derivatives in black tea manufacturing process and brewing.
A, change in chiral isomer ratio in manufacture processing. Statistically significant difference between processes was analyzed by One-way ANOVA. linalool: F = 2.708, P = 0.073; diendiol I: F = 18.306, P < 0.001; linalool oxide A: F = 20.447, P < 0.001; linalool oxide B: F = 8.068, P = 0.002; linalool oxide C: F = 3.866, P = 0.026; linalool oxide D: F = 19.083, P < 0.001. B, change in chiral isomer content in manufacture processing. Statistically significant difference between processes was analyzed by One-way ANOVA. S-linalool: F = 8.296, P = 0.001; R-linalool: F = 7.966, P = 0.002; S-diendiol I: F = 22.379, P < 0.001; R-diendiol I: F = 10.787, P < 0.001; (2S, 5S)-linalool oxide A: F = 8.528, P = 0.001; (2R, 5R)-linalool oxide A: F = 14.650, P < 0.001; (2S, 5R)-linalool oxide B: F = 13.679, P < 0.001; (2R, 5S)-linalool oxide B: F = 40.576, P < 0.001; (2S, 5R)-linalool oxide C: F = 178.898, P < 0.001; (2R, 5S)-linalool oxide C: F = 141.296, P < 0.001; (2S, 5S)-linalool oxide D: F = 271.872, P < 0.001; (2R, 5R)-linalool oxide D: F = 98.613, P < 0.001. C, impact of brewing on chiral isomer ratio. Statistically significant difference was analyzed by student's t-test. P, picking; W14, withering for 14 h; W25, withering for 25 h; R, rolling; F, fermentation; D, drying; TF, tea infusion. All the statistical analysis were performed using SPSS 29.