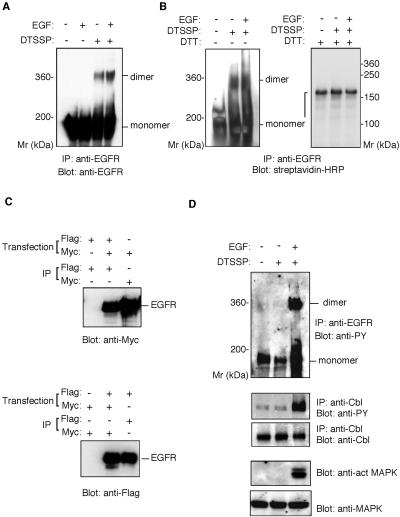
Figure 1.
Ligand-independent preformed dimer of EGFR in BE cells. (A) Cross-linking assay of the EGFR dimer. BE cells were preincubated with or without EGF, then treated with DTSSP. The cell lysates were precipitated with rabbit anti-EGFR antibody. Precipitated material was separated by 4% SDS-PAGE in the absence of reducing agents and detected by immunoblot with anti-EGFR mAb. (B) Cross-linking of surface-biotinylated EGFR. BE cells were biotinylated with sulfo-N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide-biotin, incubated with or without EGF, and then treated with DTSSP. The cell lysates were precipitated with anti-EGFR polyclonal antibody. Precipitated material was separated by SDS-PAGE in the presence or absence of 5 mM dithiothreitol and detected by immunoblot with streptavidin-HRP. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation assay of epitope-tagged EGFR. COS cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding EGFR-myc and EGFR-Flag or transfected with either one of the plasmids alone. The transfected cells were lysed and the cell lysates immunoprecipitated by rabbit anti-myc antibody or anti-Flag mAb. The precipitated materials were separated by 7% SDS-PAGE, transferred to an Immobilon membrane, and blotted with rabbit anti- myc or anti-Flag mAb. (D) Phosphorylation of EGFR, Cbl, and MAP kinase. BE cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-EGFR polyclonal antibody or anti-Cbl antibody. Precipitated materials were subjected by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-phosphotyrosine mAb or anti-Cb1 antibody. MAP kinase and phosphorylated MAP kinase were detected from the cell lysate by Western blotting using anti-MAP kinase or anti-phosphorylated MAP kinase antibody.