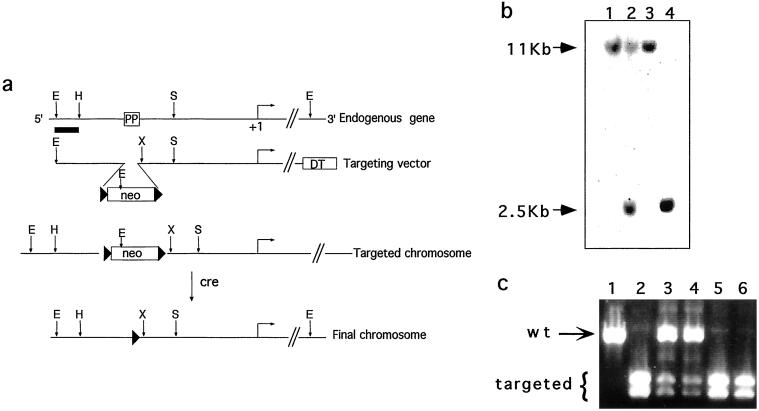
Figure 1.
Disruption of the PPARE element in the PEPCK-C gene. (a) The structures of the endogenous PEPCK gene, targeting vector, and the mutated chromosomes. The position of the PPARγ binding site in the 5′ flanking region of the gene is indicated (PP), and the horizontal arrow indicates the transcription start site (+1 bp). Restriction sites: E, EcoRI; H, HincII; X, XhoI; S, SmaI. Black triangles, loxP sites; neo, neomycin resistance gene; DT, diphtheria toxin-A chain gene. (b) Southern blot of EcoRI-digested genomic DNA from wild-type embryonic stem cells (lanes 1 and 3), targeted embryonic stem cells (lane 2), and homozygous mice (lane 4) hybridized to the probe indicated in a (as a thick line). The wild-type allele (11 kb) and targeted allele (2.5 kb) are indicated. (c) PCR products of genomic DNA using primers that span the PPARE site as specified in Methods. The products were digested with XhoI and separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. The wild-type allele (804 bp) and the doublet of the targeted allele (409 and 395 bp) are indicated.