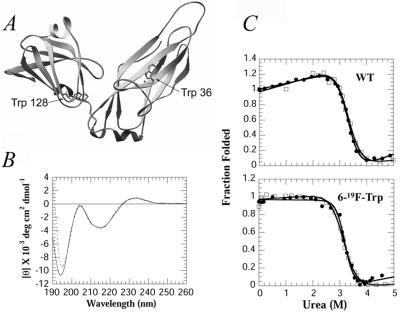
Figure 1.
(A) The crystal structure of PapD showing the location of the two tryptophan residues in the N- and C-terminal domains (3, 27). (B) Far-UV CD spectra of PapD 19F-labeled (---) and unlabeled (—) in 30 mM Mops/HCl, pH 7.0. (C) Fluorescence (●) and CD (□) changes of PapD wt (Upper) and 19F-labeled (Lower) as a function of urea. The data are normalized to the fraction folded by using the standard equation: F = ([θ/F] − [θ/F]u)/([θ/F]n − [θ/F]u), where [θ/F] represents ellipticity at 233 nm/fluorescence emission at 350 nm for fully folded (n) or unfolded (u) states.