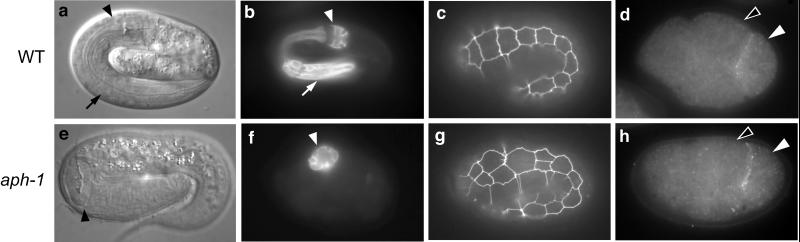
Figure 1.
aph-1 and wild-type embryos. (a) Living wild-type embryo viewed by light microscopy; the arrow indicates the anterior half of the pharynx and the arrowhead indicates the posterior half. (b) Immunostaining of pharyngeal cells; markers as in a. (c) Hypodermal cell boundaries delineated by green fluorescent protein expression; 10 cells are visible in the lateral row. (d) Four-cell embryo showing expression of the ligand APX-1. APX-1 is visible in the posterior-most cell (P2; white arrowhead) as a line contacting one of the GLP-1-expressing cells (ABp; black arrowhead); embryos oriented with the anterior to the left. (e–h) aph-1 mutant embryos staged, prepared, and labeled as above. Note the extra hypodermal cells at the first, second, and fourth positions in g. e and g are aph-1(zu147), and f and h are aph-1(zu123).