Abstract
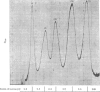
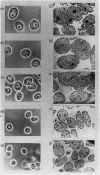
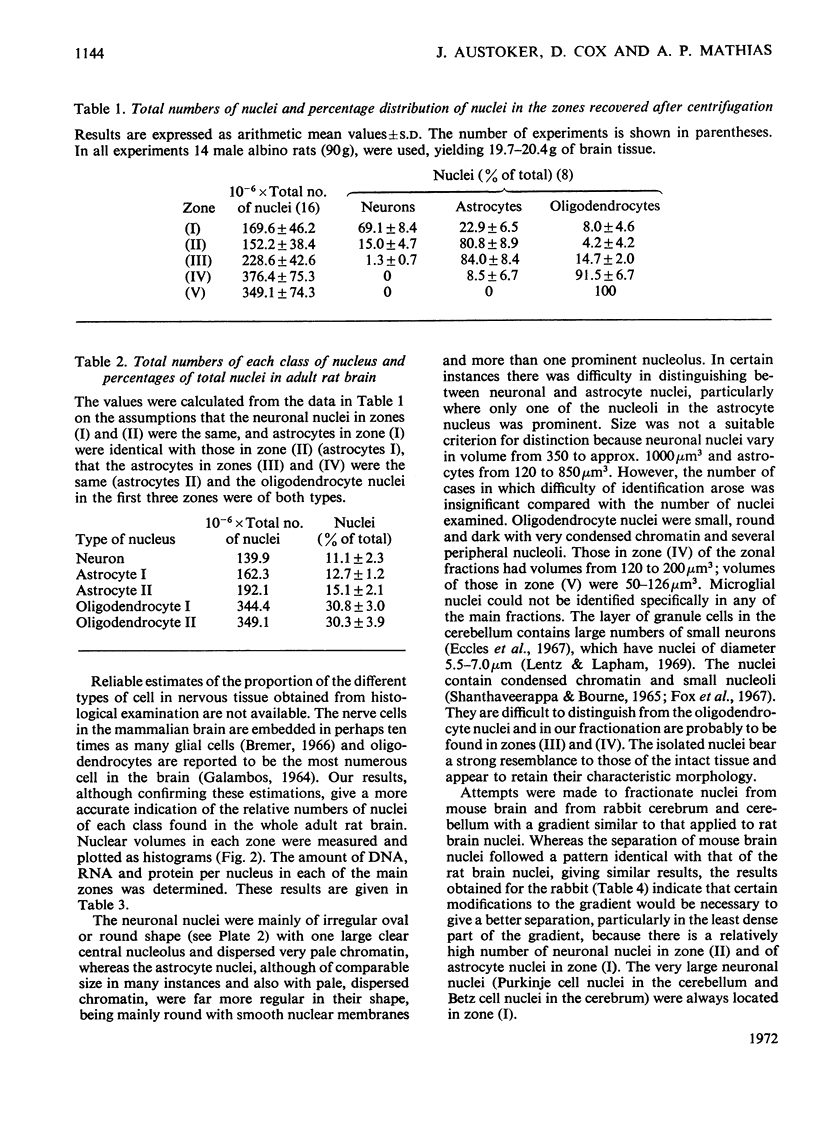
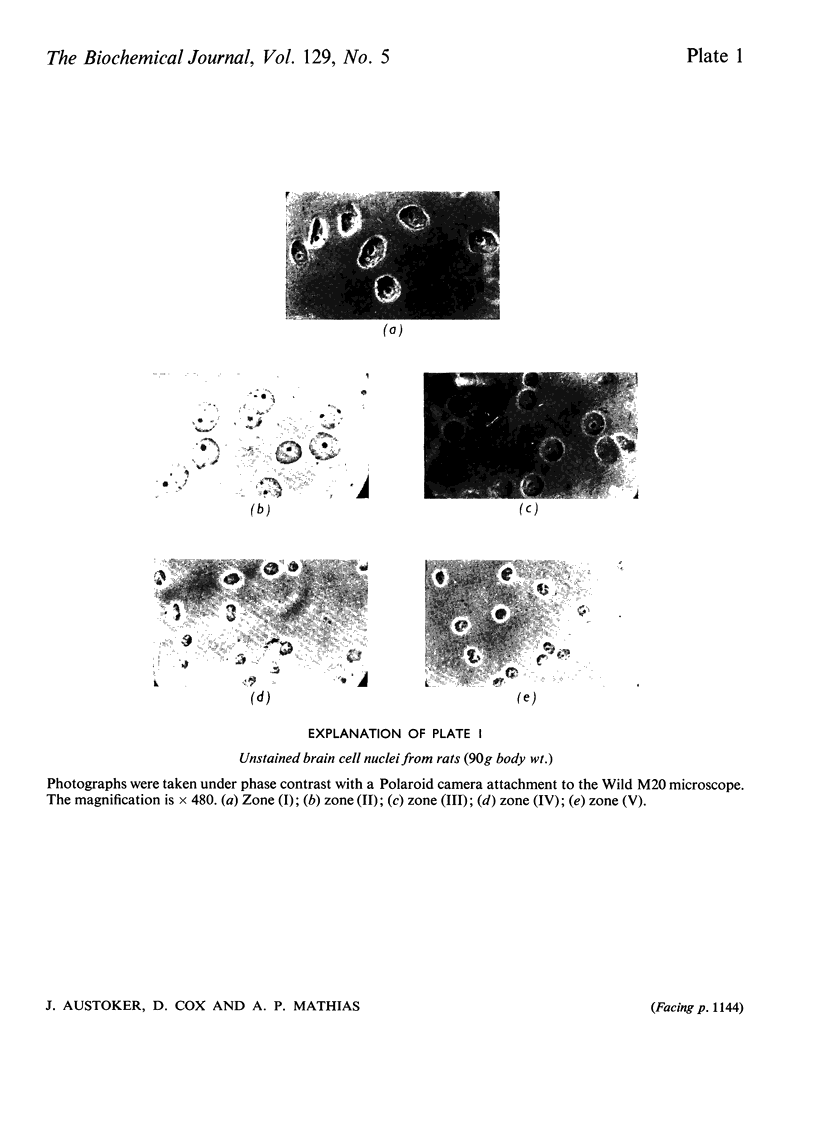
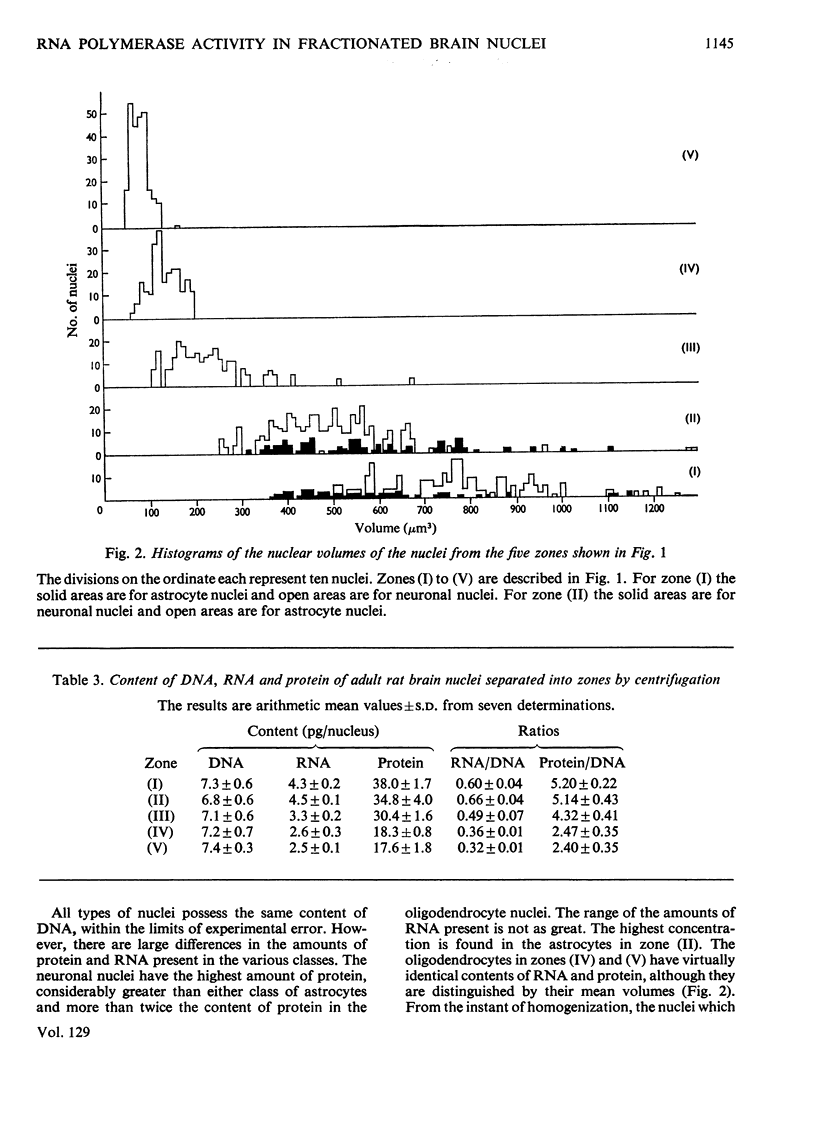
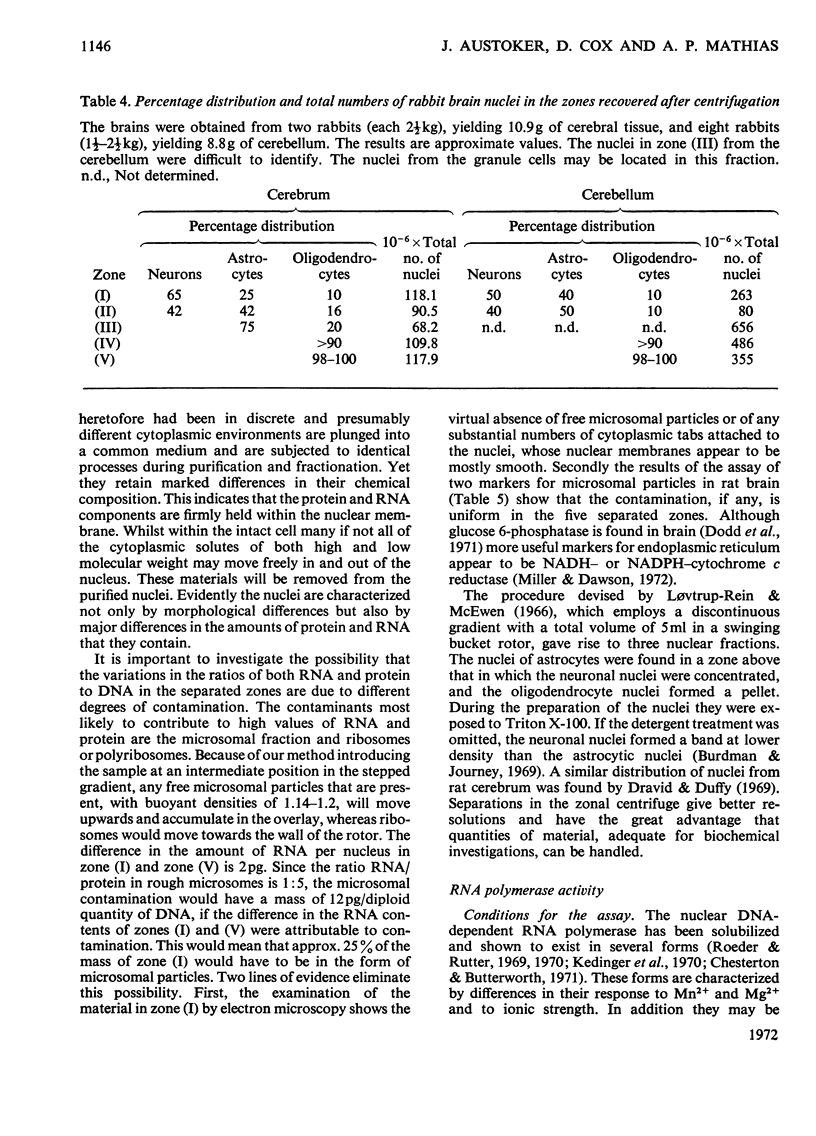
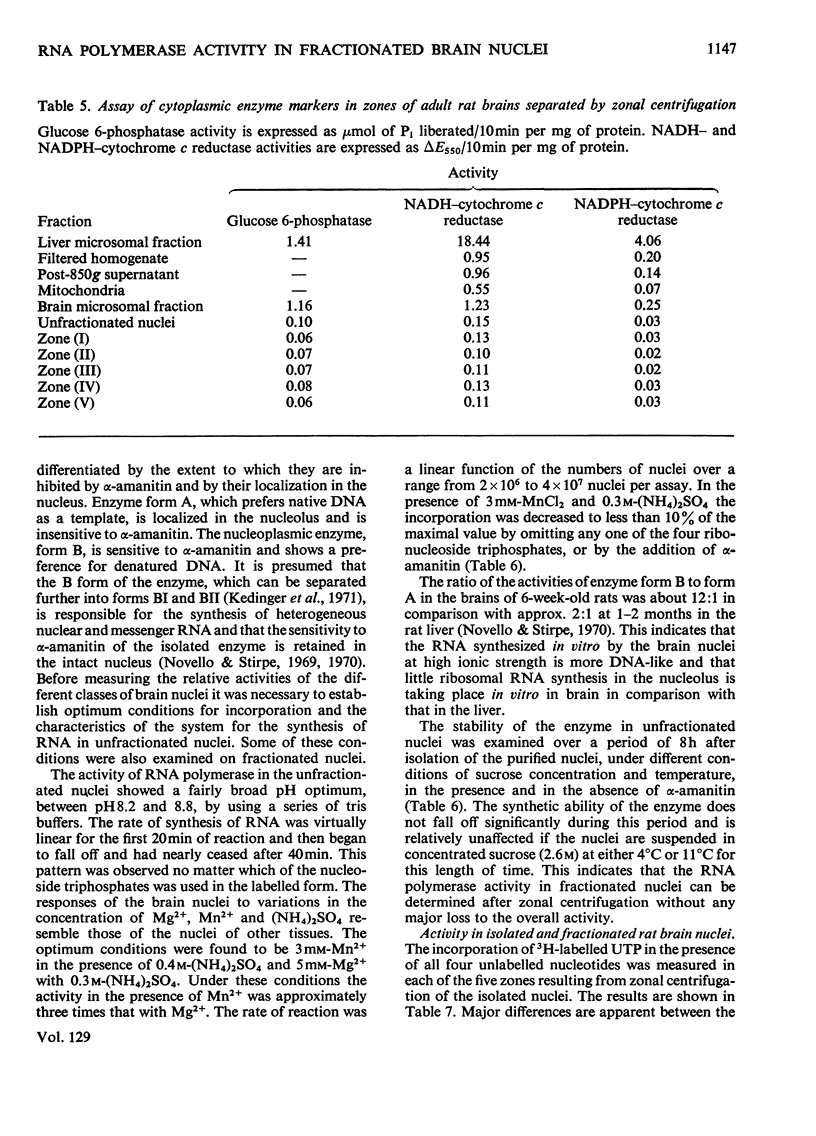
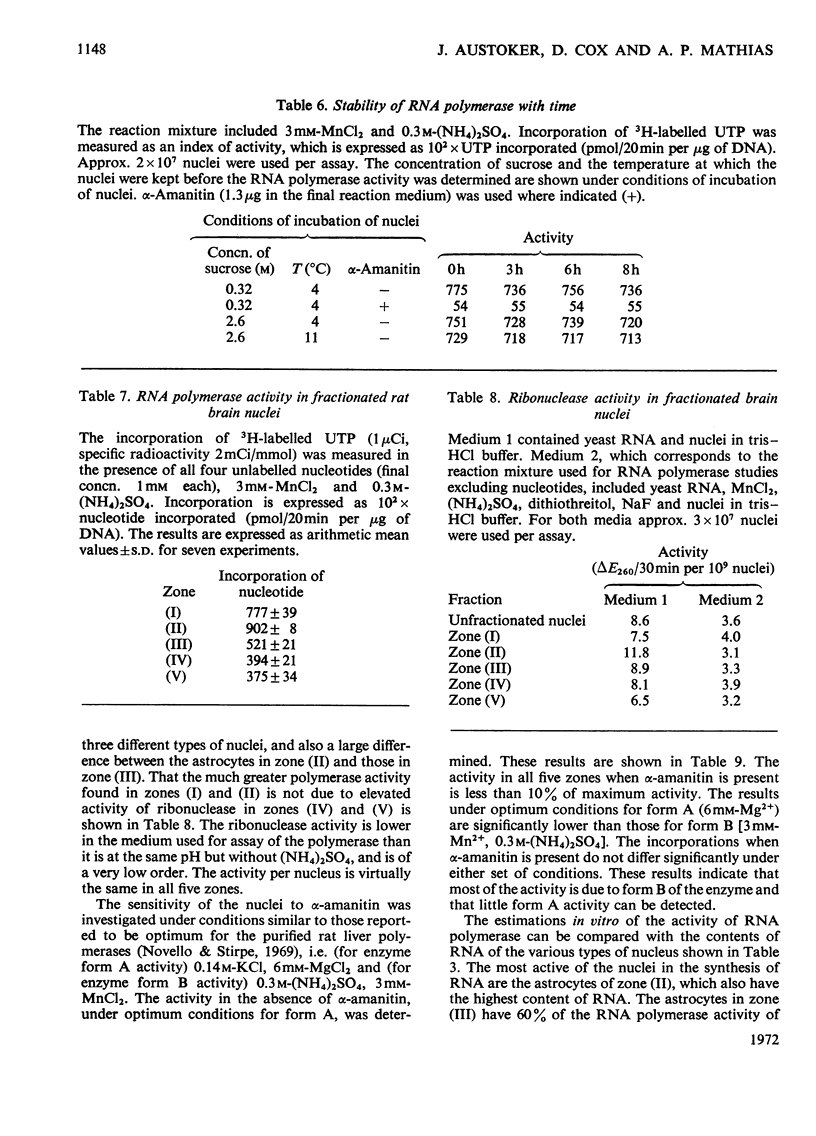
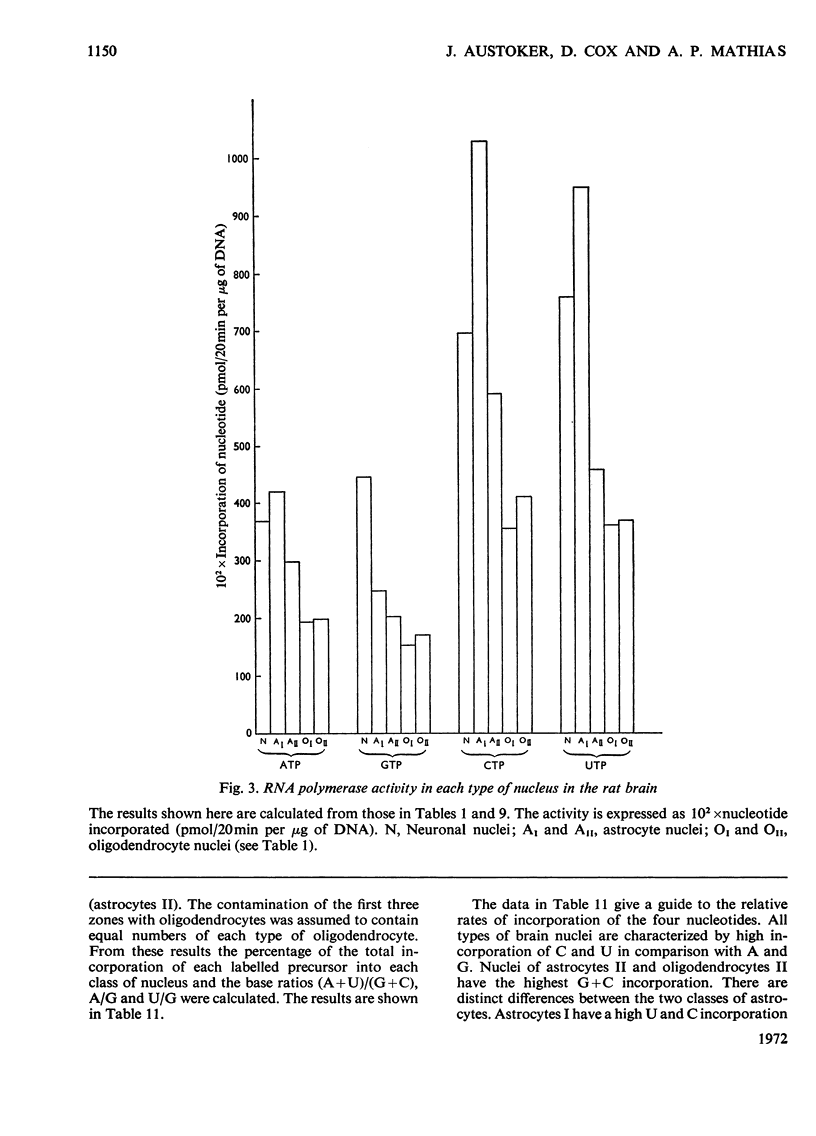
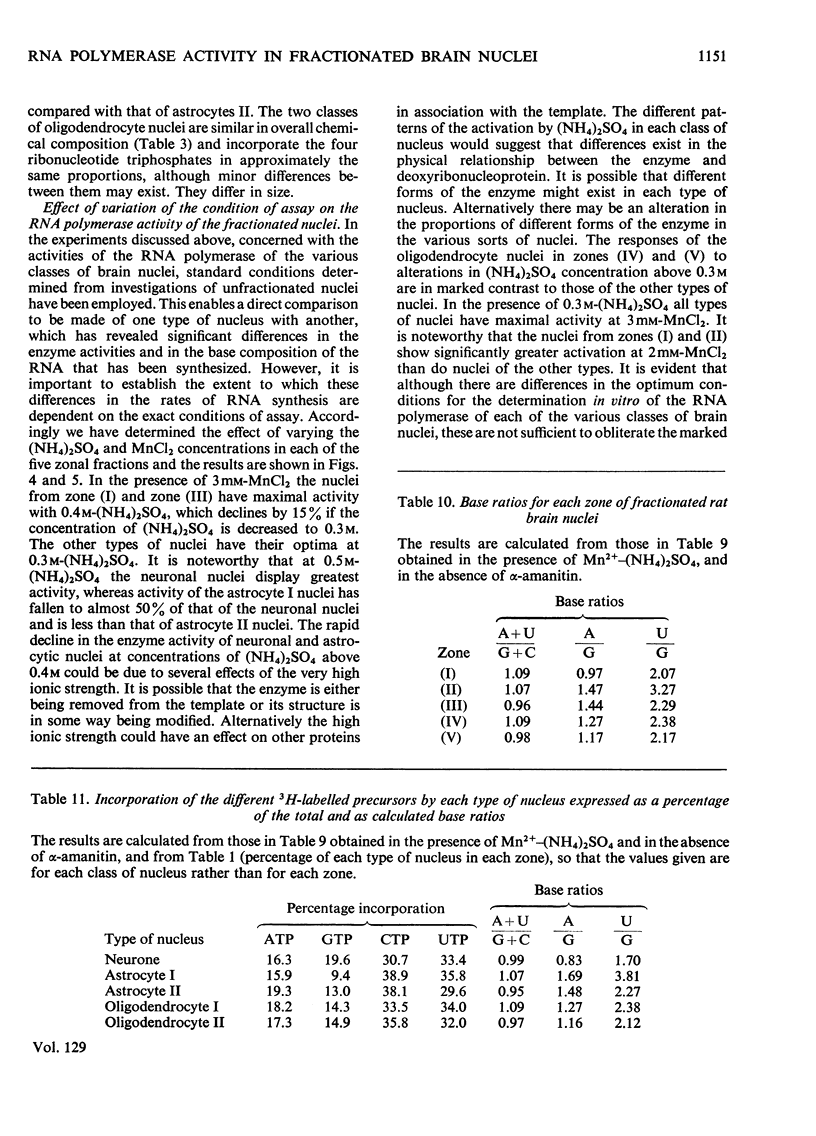
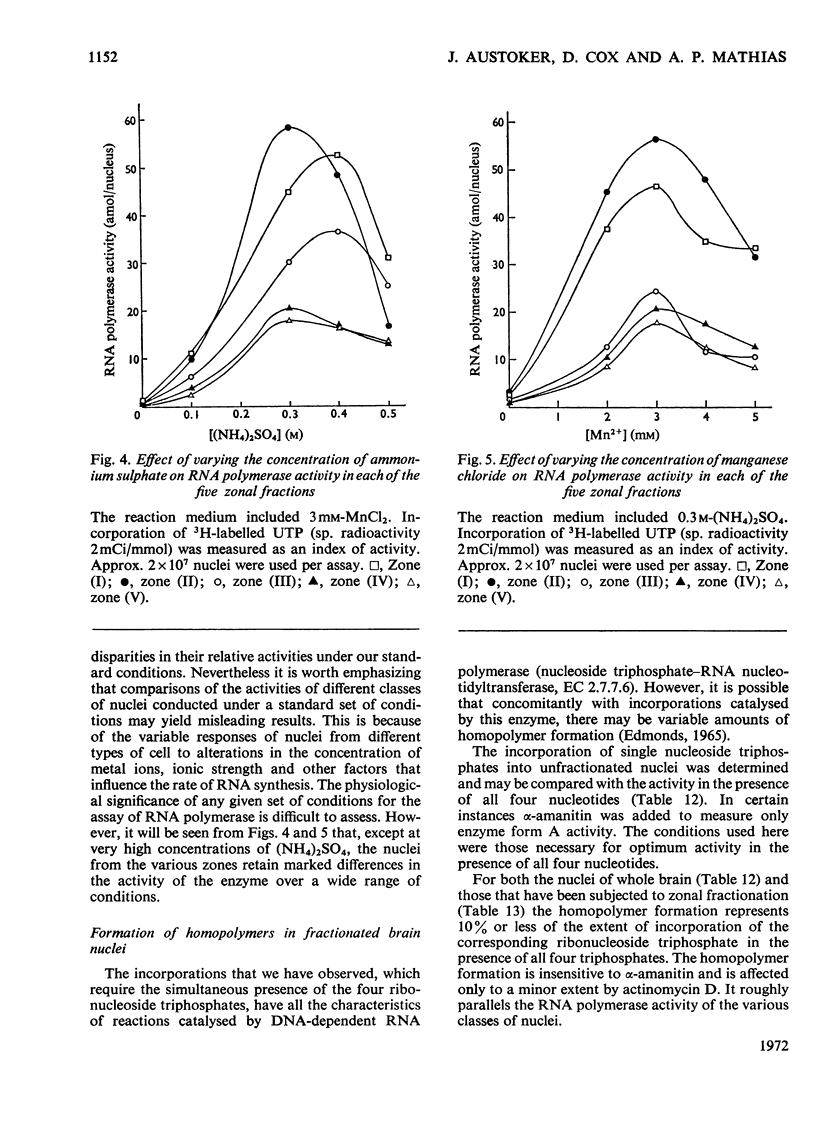
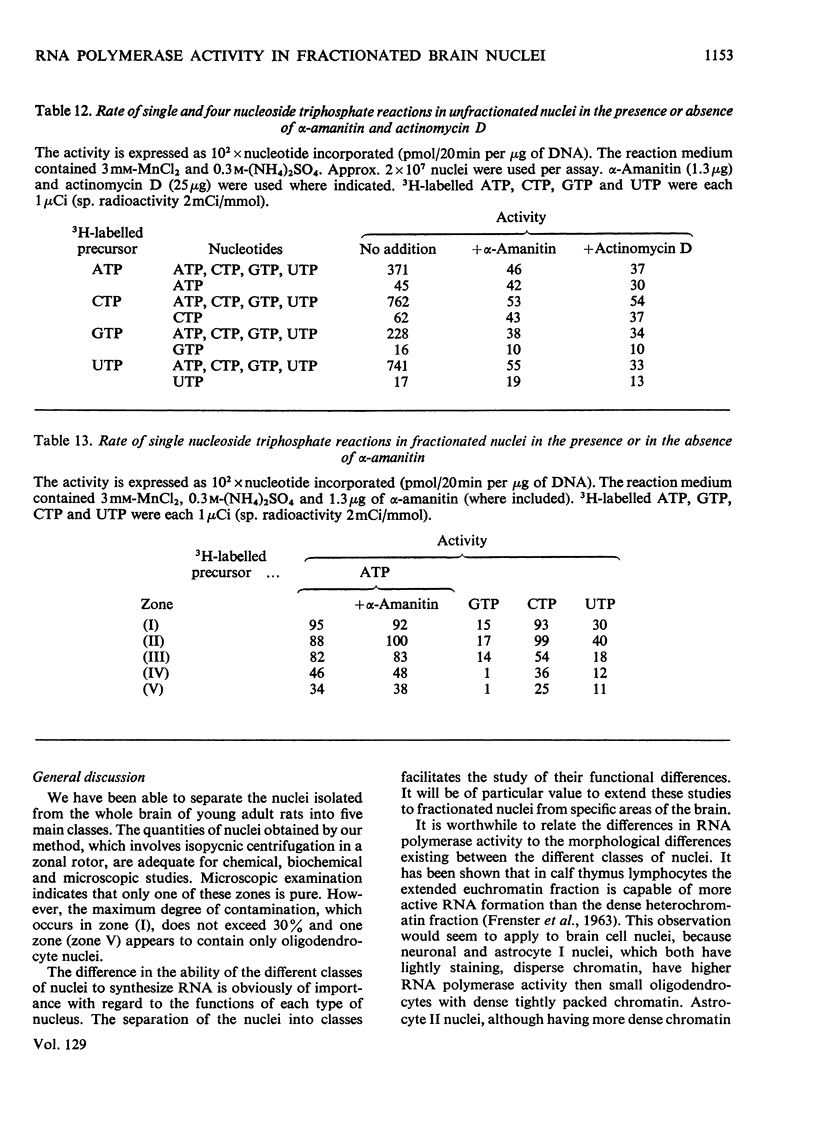
1. The nuclei of the cells of the whole rat brain have been fractionated in a B-XIV zonal rotor with a discontinuous gradient of sucrose. Five fractions were obtained. Zone (I) contained neuronal nuclei (70%) and astrocytic nuclei (23%). Zone (II) contained astrocytic nuclei (81%) and neuronal nuclei (15%). Zone (III) contained astrocytic nuclei (84%) and oligodendrocytic nuclei (15%). Zone (IV) contained oligodendrocytic nuclei (92%) and zone (V) contained only oligodendrocytic nuclei. 2. The content of DNA, RNA and protein per nucleus was determined for each zone. Although the amount of DNA per nucleus is constant (7pg) the RNA varies from 4.5 to 2.5pg/nucleus and the protein from 38 to 17.6pg/nucleus. The neuronal nuclei have the greatest amounts of protein. The oligodendrocytic nuclei have the least content of RNA and protein. 3. The effects of pH, ionic strength, and Mg2+ and Mn2+ concentration on the activity of the nuclear system for synthesis in vitro of RNA have been investigated for unfractionated nuclei. From these studies a standard set of conditions for the assay of nuclear RNA polymerase has been established. 4. The activity of the RNA polymerase in each of the zonal fractions has been determined in the presence and in the absence of α-amanitin. Zone (II) is the most active, followed by zone (I). The nuclei of zones (IV) and (V) have comparable activity, which is 40% of that of zone (II). 5. The extent of incorporation of each of the four labelled nucleoside triphosphates by the nuclei from each zone has been measured. These values have been used to calculate the base composition of the RNA synthesized in vitro in each class of nucleus. 6. The effect of changes in the condition of assay of RNA polymerase in the different classes of nuclei has been investigated. Significant differences in the response to concentrations of metal ions and ammonium sulphate have been observed. 7. Homopolymer formation in each zone of brain nuclei has been determined. The extent of formation of the four homopolymers roughly parallels the RNA polymerase activity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Roberts S. Hybridizable ribonucleic acid of rat brain. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1090533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Roberts S. Messenger ribonucleic acid of cerebral nuclei. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1111–1118. doi: 10.1042/bj1051111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Waelsch H. Nuclear RNA polymerase in brain and liver. J Neurochem. 1965 Aug;12(8):751–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdman J. A., Journey L. J. Protein synthesis in isolated nuclei from adult rat brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):493–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFT D. N., LUBRAN M. THE ESTIMATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID IN THE PRESENCE OF SIALIC ACID: APPLICATION TO ANALYSIS OF HUMAN GASTRIC WASHINGS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:612–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0950612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H.W. A new form of mammalian DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and its relationship to the known forms of the enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1971 Feb 9;12(6):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B., Brattgård S. O. A comparison between RNA metabolism of nerve cells and glia in the hypoglossal nucleus of the rabbit. J Neurochem. 1966 Oct;13(10):913–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb10287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Wall R., Tushinski R. J. An adenylic acid-rich sequence in messenger RNA of HeLa cells and its possible relationship to reiterated sites in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd P. R., Bradford H. F., Chain E. B. The metabolism of glucose 6-phosphate by mammalian cerebral cortex in vitro. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1027–1038. doi: 10.1042/bj1251027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dravid A. R., Duffy T. E. Studies on in vitro RNA synthesis in rat brain nuclei: biphasic stimulation of RNA polymerase with ammonium sulfate. Brain Res. 1969 Dec;16(2):516–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dravid A. R., Pete N., Mandel P. An enzyme system in rat brain nuclei incorporating AMP into polyadenylate. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M. A cytidine triphosphate polymerase from thymus nuclei. 1. Purification and properties of the enzyme and its polynucleotide primer. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4621–4628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENSTER J. H., ALLFREY V. G., MIRSKY A. E. REPRESSED AND ACTIVE CHROMATIN ISOLATED FROM INTERPHASE LYMPHOCYTES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1026–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. A., Hillman D. E., Siegesmund K. A., Dutta C. R. The primate cerebellar cortex: a Golgi and electron microscopic study. Prog Brain Res. 1967;25:174–225. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60965-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman E. The biochemistry of learning: an evaluation of the role of RNA and protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:605–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines M. E., Johnston I. R., Mathias A. P., Ridge D. The synthesis of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide and poly (adenosine diphosphate ribose) in various classes of rat liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):881–887. doi: 10.1042/bj1150881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines M. E., Johnston I. R., Mathias A. P. The role of rat liver nuclear DNA polymerase and its distribution in various classes of liver nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1970 Sep 24;10(2):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman C. J., Lapham L. W. Neuronal polyploidy and nuclear volumes in the cat central nervous system. Brain Res. 1969 Sep;15(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Stevenin J., Jund R., Judes C., Mandel P. Rapidly-labelled ribonucleic acids in brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):619–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston I. R., Mathias A. P., Pennington F., Ridge D. Distribution of RNA polymerase activity among the various classes of liver nuclei. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):668–672. doi: 10.1038/220668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston I. R., Mathias A. P., Pennington F., Ridge D. The fractionation of nuclei from mammalian cells by zonal centrifugation. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;109(1):127–135. doi: 10.1042/bj1090127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Kurokawa M. Studies on ribonucleic acid and homopolyribonucleotide formation in neuronal, glial and liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(4):599–609. doi: 10.1042/bj1160599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Nuret P., Chambon P. Structural evidence for two alpha-amanitin sensitive RNA polymerases in calf thymus. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapham L. W. Tetraploid DNA content of Purkinje neurons of human cerebellar cortex. Science. 1968 Jan 19;159(3812):310–312. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3812.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz R. D., Lapham L. W. A quantitative cytochemical study of the DNA content of neurons of rat cerebellar cortex. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):379–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovtrup-Rein H., McEwen B. S. Isolation and fractionation of rat brain nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):405–415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovtrup-Rein H. Synthesis of nuclear RNA in nerve and glial cells. J Neurochem. 1970 Jul;17(7):853–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Moore W. J., Thompson R. J. Isolation and characterization of ribonucleic acid from cerebral cortex of rat. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1283–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel P., Dravid A. R., Pete N. Poly C synthetase activity in the particulate fraction of rat brain nuclei. J Neurochem. 1967 Mar;14(3):301–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. K., Dawson R. M. Can mitochondria and synaptosomes of guinea-pig brain synthesize phospholipids? Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):805–821. doi: 10.1042/bj1260805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NURNBERGER J. I., GORDON M. W. The cell density of neural tissues: direct counting method and possible applications as a biologic referent. Prog Neurobiol. 1957;2:100–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novello F., Stirpe F. Experimental conditions affecting ribonucleic acid polymerase in isolated rat liver nuclei. Effect of nucleoside triphosphate concentration, temperature, ammonium sulphate and heparin. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):721–727. doi: 10.1042/bj1120721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novello F., Stirpe F. Simultaneous assay of RNA polymerase I and II in nuclei isolated from resting and growing rat liver with the use of alpha-amanitin. FEBS Lett. 1970 May 11;8(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo A. O., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. Modification of ribonucleic Acid synthesis in nuclei isolated from normal and regenerating liver: some effects of salt and specific divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):743–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanthaveerappa T. R., Bourne G. H. The thiamine pyrophosphatase technique as an indicator of the morphology of the Golgi apparatus in the neurons. IV. Studies on the cerebellum of rat and squirrel monkey. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Dec 10;68(5):699–710. doi: 10.1007/BF00340095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetten M. R., Ghosh S. B. Different properties of glucose-6-phosphatase and related enzymes in rough and smooth endoplasmic reticular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]