Abstract
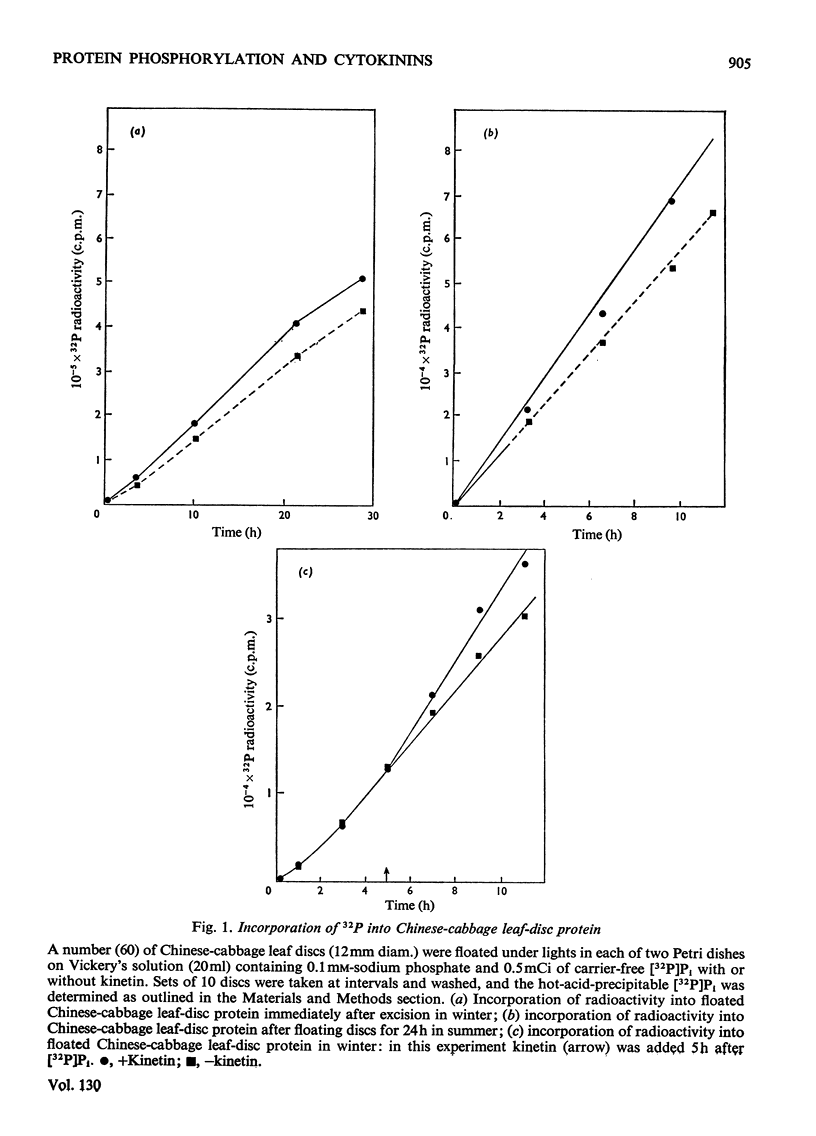
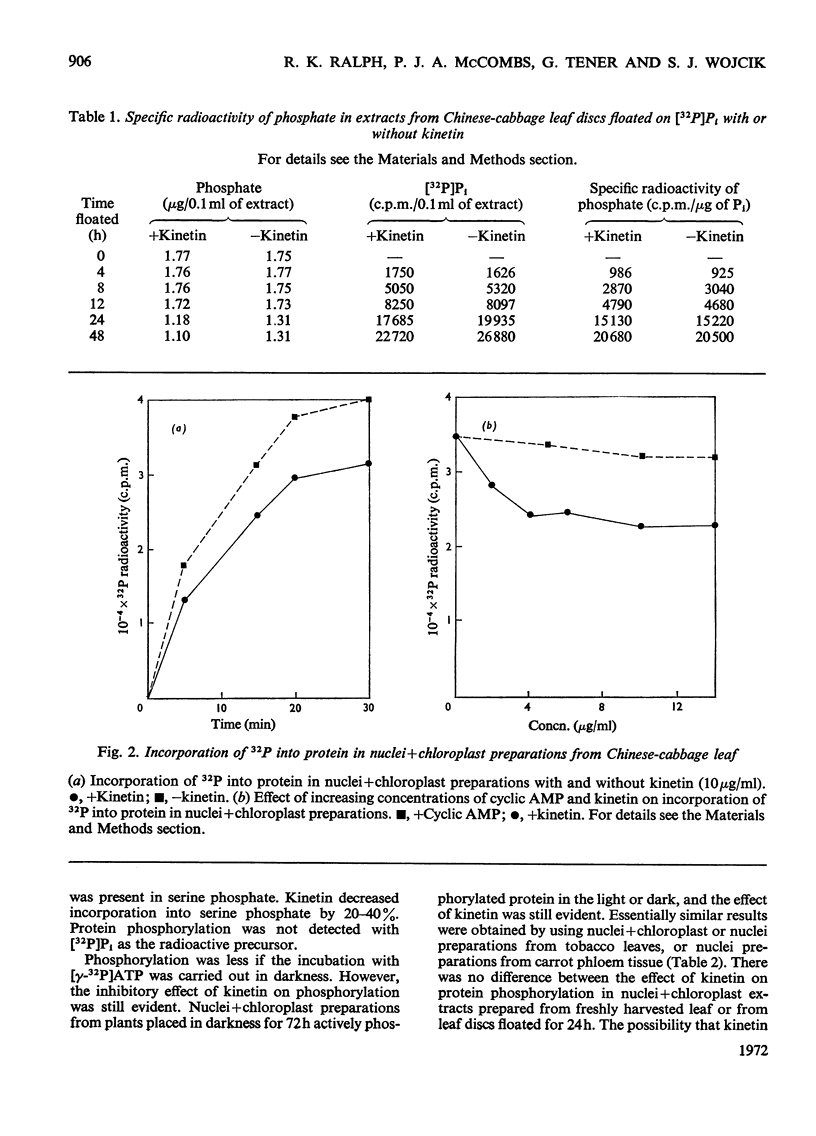
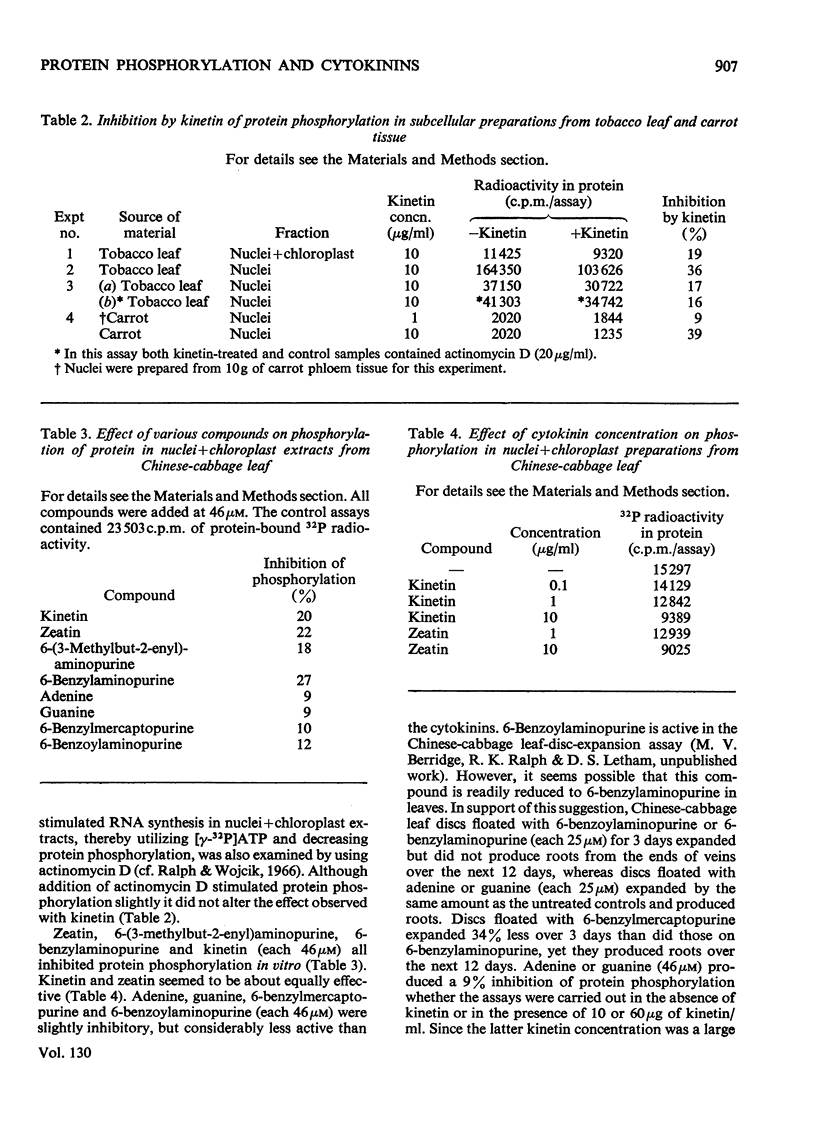
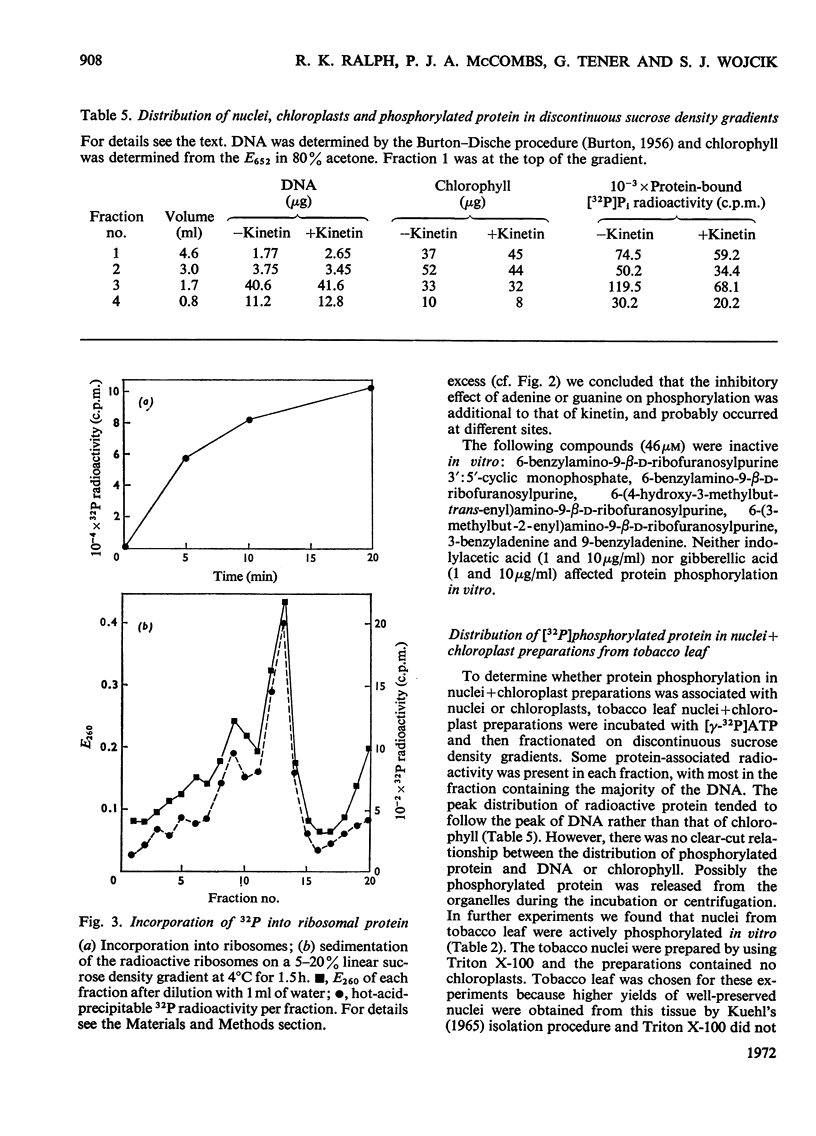
Kinetin stimulated phosphorylation of protein in floated Chinese-cabbage leaf discs, but inhibited protein phosphorylation in nuclei+chloroplast extracts from Chinese-cabbage or tobacco leaves. Kinetin also inhibited protein phosphorylation in isolated tobacco nuclei or nuclei from carrot secondary-phloem tissue. Purified Chinese-cabbage leaf ribosomes exhibited protein kinase activity which was inhibited by kinetin and zeatin. The ribosome-associated kinase responded to kinetin and zeatin differently from that associated with nuclei+chloroplast preparations. Protein phosphorylation in vitro was not affected by adenosine 3′:5′-cyclic monophosphate, indol-3-ylacetic acid or gibberellic acid. It was only inhibited by N9-unsubstituted purines, among which the known cytokinins were the most effective inhibitors. The results are discussed in relation to possible similarities between the effects of cytokinins in plant tissues and the effects of adenosine 3′:5′-cyclic monophosphate in animal tissues. Both compounds appear to modify the activity of protein kinases and both affect many different cellular processes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIELESKI R. L. SEPARATION OF PHOSPHATE ESTERS BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY AND ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Aug;12:230–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. V., Ralph R. K., Letham D. S. The binding of kinetin to plant ribosomes. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):75–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1190075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. V., Ralph R. K. Some effects of kinetin on floated Chinese cabbage leaf discs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):266–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blat C., Loeb J. E. Effect of glucagon on phosphorylation of some rat liver ribosomal proteins in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 15;18(1):124–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80425-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M., Williams R. C., Jr, Feizi T., Kunkel H. G. Light chain sequences of human IgM cold agglutinins (variable-region subgroups amino-acid sequence-kappa light chain-N-terminal). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):40–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galantay E., Weber H. P. Synthese von (plus or minus)-B-Homoöstron. Experientia. 1969 Jun 15;25(6):571–572. doi: 10.1007/BF01896514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Kuo J. F., Miyamoto E. Studies on the mechanism of action of cyclic AMP in nervous and other tissues. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;9:113–125. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(71)80040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht S. M., Bock R. M., Schmitz R. Y., Skoog F., Leonard N. J., Occolowitz J. L. Question of the ribosyl moiety in the promotion of callus growth by exogenously added cytokinins. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4224–4228. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman W. S. Nonphotosynthetic Light Requirement in Lemna minor and Its Partial Satisfaction by Kinetin. Science. 1957 Jul 26;126(3265):165–166. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3265.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamisaka S., Masuda Y. Stimulation of auxin-induced cell expansion in plant tissue by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Naturwissenschaften. 1970 Nov;57(11):546–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00625331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipmann F. Effects of cyclic AMP, its mechanism of action, and comments on the energetics of its 3'-phosphate bond. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;9:5–16. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(71)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH B. B. The estimation of inorganic phosphate in the presence of adenosine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:357–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90607-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS R. E. Properties of nucleoprotein fractions isolated from turnip yellow mosaic virus preparations. Virology. 1960 Dec;12:521–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier D., Santhanam K., Wagle S. R. Studies on the inhibition of amino acid incorporation into protein by isolated rat liver ribosomes by protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1881–1886. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten J., Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP levels in fibroblasts: relationship to growth rate and contact inhibition of growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep;44(5):1192–1198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard C. J. Influence of gibberellic acid on the incorporation of 8-14C adenine into adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in barley aleurone layers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 24;201(3):511–512. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph R. K., Bullivant S., Wojcik S. J. Evidence for the intracellular site of double-stranded turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph R. K., Wojcik S. J. Synthesis of double-stranded viral RNA by cell-free extracts from turnip yellow mosaic virus-infected leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 19;119(2):347–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D., Mascarenhas J. P. Auxin-induced synthesis of cyclic 3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate in Avena coleoptiles. Life Sci II. 1971 Aug;10(15):879–885. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Difference in the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in normal and transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):14–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio236014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Restoration of contact-inhibited growth to transformed cells by dibutyryl adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1316–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava B. I. Cytokinins in plants. Int Rev Cytol. 1967;22:349–387. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61839-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULI V., DILLEY D. R., WITTWER S. H. N6-BENZYLADENINE: INHIBITOR OF RESPIRATORY KINASES. Science. 1964 Dec 11;146(3650):1477–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3650.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Gill G. N., Abrass I. B., Garren L. D. Phosphorylation of ribosome-associated protein by an adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase: location of the microsomal receptor and protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


