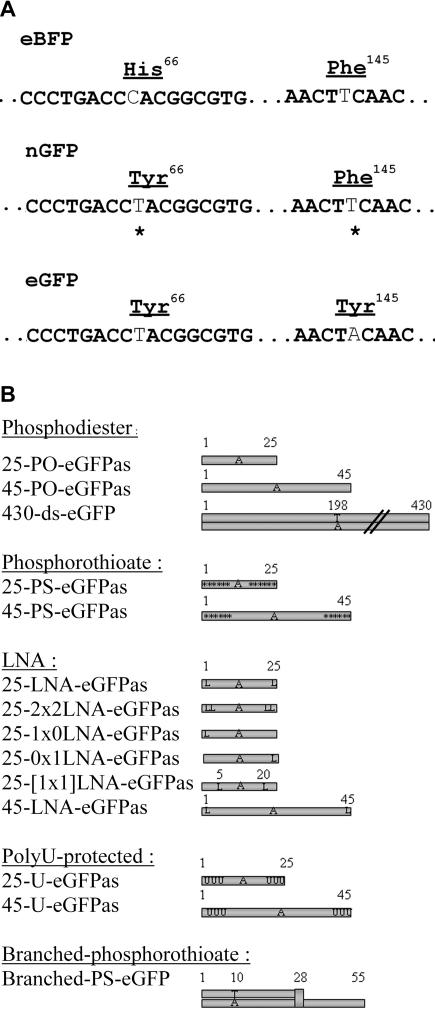
Figure 1.
Features of assay for measuring gene editing. (A) Sequence of eBFP and eBFP converted into a new GFP (nGFP) coding Tyr66 and Phe145. eGFP sequence is also indicated to show the difference from eBFP and nGFP at codon 145. (B) Schematic representation of ONs tested for targeted mutagenesis. Nomenclature: as, antisense; s, sense; ds, double-stranded; PO, phosphodiester; PS, six phosphorothioate linkages starting from 5′ and 3′ ends; asterisk, phosphorothioate linkage; L, LNA nucleotide; LNA, LNA nucleotide at 5′ and 3′ end position; 1x0-LNA, LNA nucleotide at 5′ end only; 0x1-LNA, LNA at 3′ end only; [1x1]-LNA, LNA nucleotides at internal nucleotide positions 5 and 20; U, three 2′-O-methyl uracyl RNA base starting from 5′ and 3′ ends; branched-PS-eGFP, ON with specific structure consisting of double-stranded DNA with 5′ single-stranded DNA tail coupled together by a baseless deoxyribose branching monomer described as B7 ON in (5). 430-ds-eGFP: 1–430 bp of eGFP sequence. Sequences were as follows: 25-eGFPas, 5′-ACTGCACGCCGTAGGTCAGGGTGGT-3′; 25-eGFP-s, 5′-ACCACCCTGACCTACGGCGTGCAGT-3′; 45-eGFPas, 5′-CGGCTGAAGCACTGCACGCCGTAGGTCAGGGTGGTCACGAGGGTG-3′; 45-eGFPs, 5′-CACCCTCGTGACCACCCTGACCTACGGCGTGCAGTGCTTCAGCCG-3′; 25-PDEas, 5′-ACTTTCTGCTACGTAGGTTGGAAGG-3′; 25-PDEs, 5′-CCTTCCAACCTACGTAGCAGAAAGT-3′.