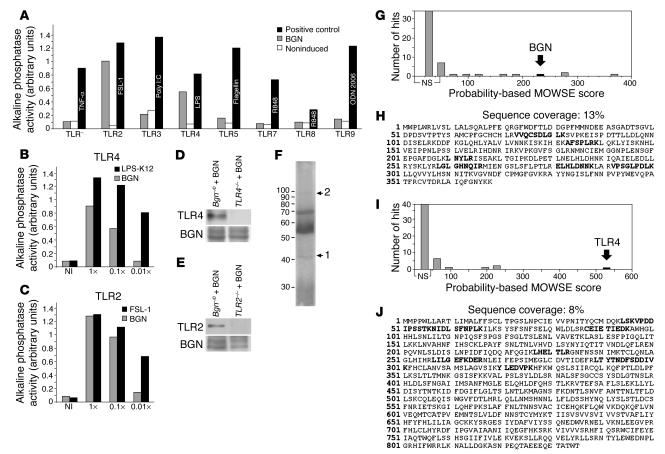
Figure 5.
Interaction of BGN with TLR4 and TLR2 in macrophages. (A) Screening for BGN-induced (10 μg/ml) activation of NF-κB in 293-TLR cells expressing only 1 type of TLR and alkaline phosphatase as reporter gene (gray bars). An HEK293 cell line expressing only the reporter gene was used as control (TLR–). As positive control, each cell line was induced with a specific ligand (black bars). Noninduced TLR clones were used as negative controls (white bars). TLR activation is shown as activity of the secreted alkaline phosphatase in arbitrary units. (B and C) Dose-response analysis of the effect of BGN (gray bars; 1× equals 10 μg/ml) on the activation of TLR4 (B) and TLR2 (C). “NI” indicates a noninduced TLR cell line. Black bars represent positive controls (1× equals 100 ng/ml of LPS-K12 or FSL-1). (D and E) Immunoprecipitation for BGN after incubation of Bgn–/0 or TLR4–/– (D) or TLR2–/– macrophages (E) with BGN (4 μg/ml) in the presence of a cross-linker, followed by Western blot for TLR4 (D, top panel) or TLR2 (E, top panel). The bottom panels represent Western blots for BGN core protein after chondroitinase ABC treatment. (F) Colloidal Coomassie G250–stained SDS-PAGE indicating bands obtained by immunoprecipitation and analyzed by ESI/MS/MS. (G–J) ESI/MS/MS of bands labeled in F as 1 (G and H) and 2 (I and J) recognized human BGN with a probability-based score of 221 (G) and with a sequence coverage of 13% (H) and mouse TLR4 with a probability-based score of 528 (I) and with a sequence coverage of 8% (J). MOWSE, molecular weight search.