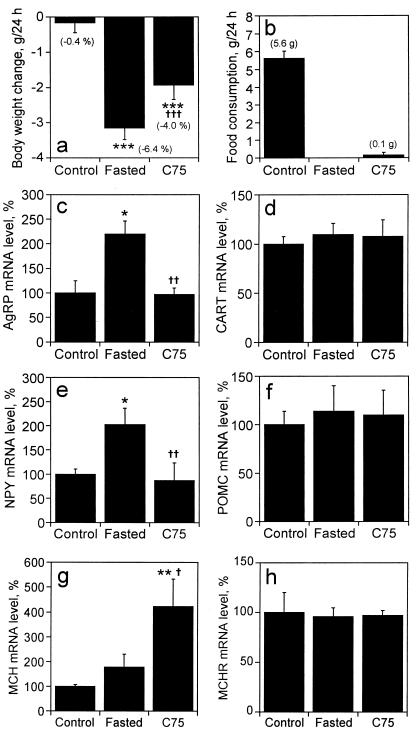
Figure 3.
Effect of C75 on hypothalamic neuropeptide mRNA levels in ob/ob mice. ob/ob mice were fasted (n = 6), injected i.p. with vehicle (n = 6) (control) or injected i.p. with C75 (30 mg/kg body weight) (n = 6) beginning 3 h before “lights off”; the latter two groups were fed ad libitum. Twenty-four hours after injection, body weight change (a) and food consumption (b) were determined and hypothalamic tissue was dissected and quickly frozen. Total hypothalamic RNA (5 μg) was mixed with a probe mixture containing: [32P]UTP-labeled cRNAs for AgRP (c), CART (d), NPY (e), POMC (f), MCH (g), and MCHR (h) mRNAs, and subjected to the RNase protection assay protocol. Protected fragments were separated by urea-PAGE and exposed to an imaging plate for 24 h. Radioactivity in the gel bands was quantified, normalized to the cyclophilin signal, and expressed as percent change relative to the mRNA level of control mice. Values are shown as means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, and ***, P < 0.001 vs. control group; †, P < 0.05, ††, P < 0.01, and †††, P < 0.001 vs. fasted group.