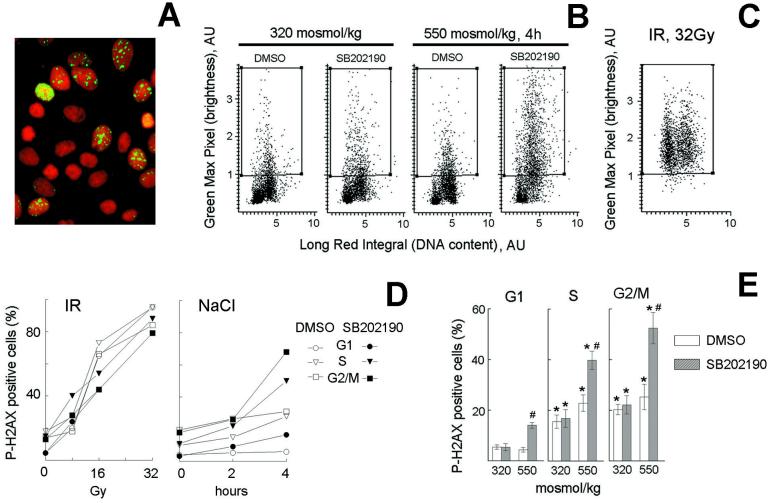
Figure 5.
Abrogation of G2 checkpoint by p38 inhibition induces DNA damage with a cell cycle distribution different from that produced by ionizing radiation (IR). mIMCD3 cells were preincubated with DMSO or SB202190 (10 μM) for 30 min, then, for osmotic stress, the media were replaced for 2 or 4 h with identical ones or with otherwise identical ones to which NaCl was added to total osmolality of 550 milliosmol/kg; for ionizing radiation, cells were irradiated with indicated levels, then returned to the incubator for 20 min. Cells were stained with PI for DNA content (red) and with antiphospho-H2AX (green) to detect DNA breaks. (A) Images of cells stained with antiphospho-H2AX and PI, illustrating localized nuclear antiphospho-H2AX staining when NaCl is added in presence of SB202190. (B and C) Representative cytograms plotting maximal green fluorescence intensity (phospho-H2AX) in the nucleus vs. red fluorescence integral (DNA content). (D and E) G1, S, and G2/M cells were identified, on the basis of their DNA content and the percent of cells in each phase of cell cycle containing localized bright green nuclear fluorescence, illustrated in A, was determined by their elevated maximal green fluorescence intensity (i.e., cells in the boxes in B and C). (D) Representative experiments. (E) Analysis of H2AX phosphorylation in G1, S, and G2/M after 4 h of elevated NaCl (mean ± SEM, n = 6). *, significantly different from G1 (P < 0.01). #, significantly different from control with DMSO (P < 0.01).