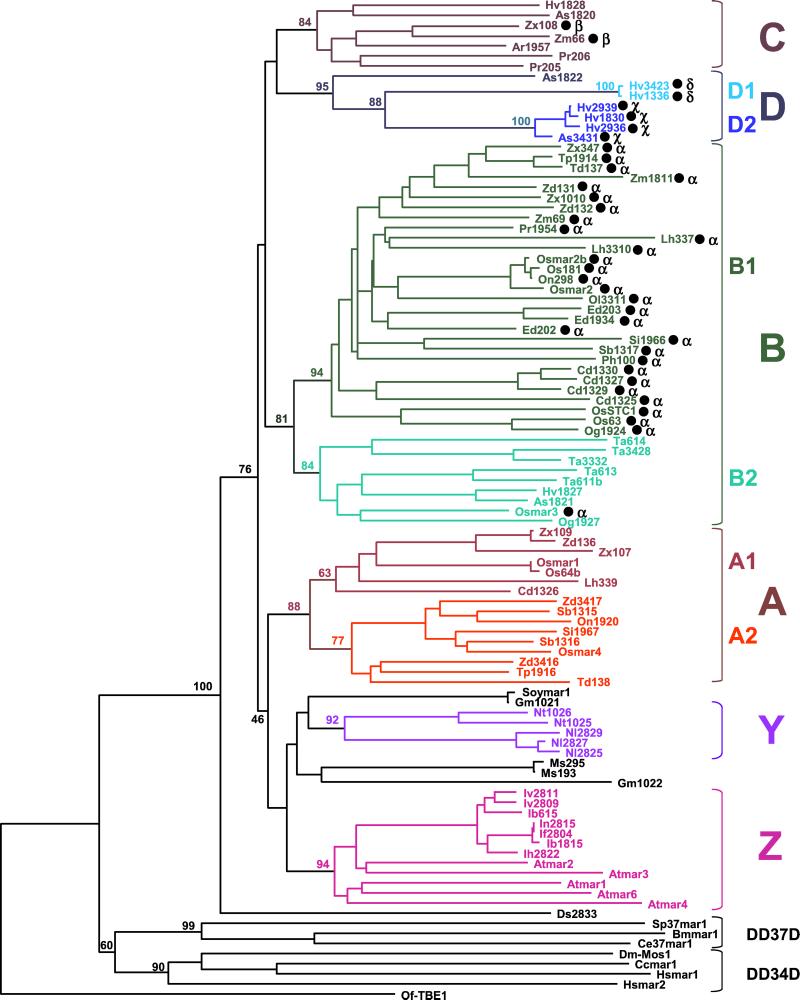
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic relationships of 91 plant MLE transposase fragments. This NJ tree was generated from a multiple alignment of conceptually translated transposase sequences, including 81 plant transposase fragments isolated by PCR (GenBank accession nos. AF432513–AF432593) and 10 obtained from database searches [Osmars, Soymars, and Atmars; see Table 2 (www.pnas.org) for accession nos.]. The corresponding regions of several animal MLE transposases from diverse subfamilies (9) and the distantly related Tc1/mariner-like transposase from the ciliate transposon TBE1 (7) were also included in this analysis [see Table 2 (www.pnas.org) for description]. Sequences were named according to the species initials followed by the number of the clone or the suffix -mar, following the nomenclature introduced by Robertson et al. (9) [see Tables 1 and 2 (www.pnas.org) for abbreviations]. A black dot after a name indicates that a predicted intron was removed from the nucleotide sequence. Introns occurred at four positions (α, β, χ, δ ; see text and Fig. 4b). Bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) are shown for the major nodes of the tree. Groupings defining lineages and sublineages of plant MLE transposases are emphasized by capital letters and different colors. Monocots, Poaceae: Ph, P. lappulaceus; Pr, P. radiciflora; Ar, Arundinaria simonii; Lh, Litachne humilis; Ed, Ehrarhta dura; Os, O. sativa, On, O. nivara; Og, O. grandiglumis; Ta, Triticum aestivum; Hv, Hordeum vulgare; As, Avena sativa; Cd, C. dactylon; Si, S. italica; Sb, S. bicolor; Td, Tripsacum dactyloides; Tp, Tripsacum pilosum; Zd, Z. diploperennis, Zx, Z. mays mexicana; Zm, Z. mays mays. Monocots Iridaceae: Nl, N. longifolia; Ib, I. brevicaulis; If, I. fulva; Ih, I. hybrida; In, I. nelsonii; Iv, I. verna. Dicots: Ds, Dianthus sp.; Gm, Glycine max; Ms, Medicago sativa; At, A. thaliana; Nt, N. tabacum. Insects Diptera Sp, Sarcophaga peregrina; Cc, Ceratitis capitata; insect Lepidoptera: Bm, Bombyx mori; nematode Ce, C. elegans; Hs, H. sapiens; ciliate: Of, Oxytricha fallax.