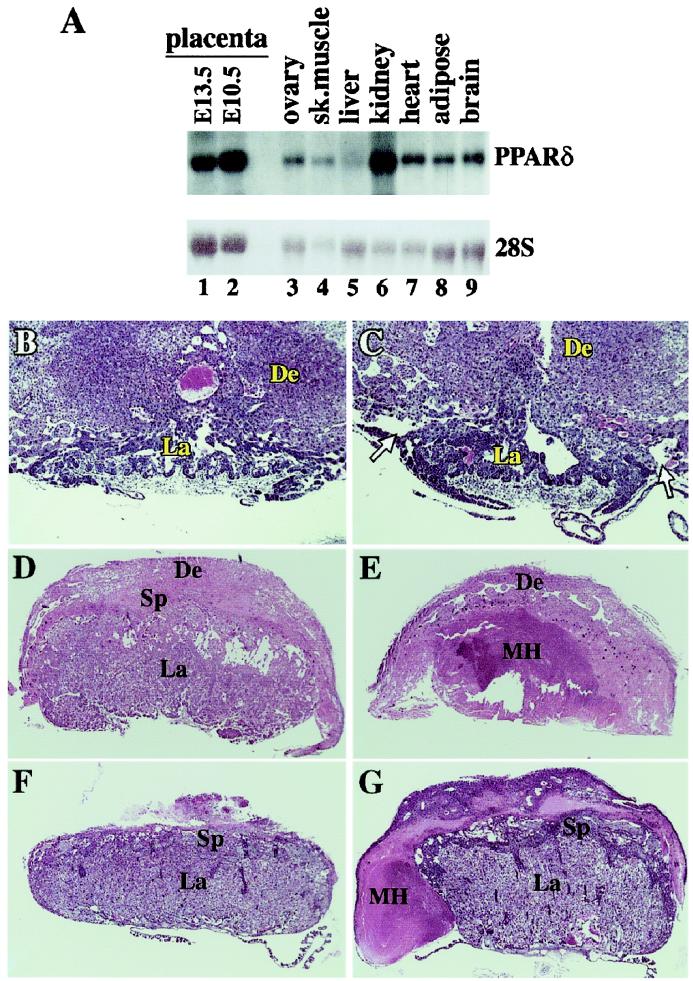
Figure 2.
Pathologies of PPARδ null placentas. (A) Mouse PPARδ tissue blot. Note the high PPARδ levels in two different stages of placental development (E10.5, E13.5), superior to most tissues, except kidney. (B and C) wt and PPARδ null placentas at E9.5. Arrows in C denote the abnormal detachment of the PPARδ null placenta from the decidua. (D and E) wt and PPARδ null placentas at E12.5. The inner core of the mutant placenta contains a massive maternal hematoma (MH) and is completely devoid of trophoblast cells. (F and G) wt and PPARδ null placentas at E14.5. The mutant placenta is surrounded by a maternal hematoma (MH). De, decidua; Sp, spongiotrophoblast layer; La, placental labyrinth; Th, thrombus. (Magnifications: B and C: ×20; D and E: ×11; F and G: ×7.)