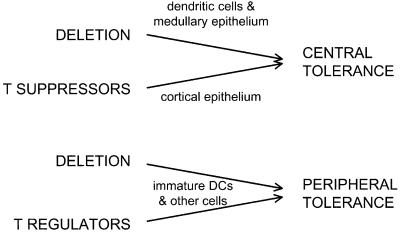
Figure 1.
Central and peripheral mechanisms for avoiding horror autotoxicus via T lymphocytes. In the thymus (central tolerance) and in other parts of the body (peripheral tolerance), self-reactive T cells can either be eliminated (deleted) or regulated (suppressed) by other T cells. Several types of antigen-presenting cells can bring about tolerance as shown by the arrows. DCs play a pervasive role, particularly for dying cells and innocuous self and environmental proteins that have to be captured and processed before presentation (as MHC class I and II–peptide complexes) to antigen receptors on T cells.