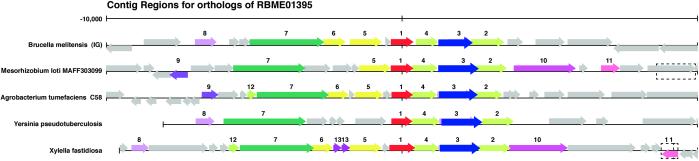
Figure 1.
The VirB operon of the type IV secretion system in B. melitensis is shown using the “pinned region” tool from ERGO, which exploits the occurrence of best paired bidirectional hits between ORFs among different organisms. The pinned region for VirB8 (red arrow) shows the type IV secretion cluster from Agrobacterium, Mesorhizobium, Yersinia, and Xylella sp. Identically colored arrows represent similar ORFs. Functions according to numbers are channel protein VirB8 homolog (no. 1), ATPase VirB11 homolog (no. 2), channel protein VirB10 homolog (no. 3), channel protein VirB9 homolog (no. 4), channel protein VirB6 homolog (5), attachment-mediating protein VirB5 homolog (no. 6), ATPase VirB4 homolog (no. 7), attachment-mediating protein VirB1 homolog (no. 8), hypothetical protein (no. 9), ATPase VirD4 homolog (no. 10), DNA recombination protein (no. 11), channel protein VirB3 protein (no. 12), and hypothetical exported protein (no. 13).