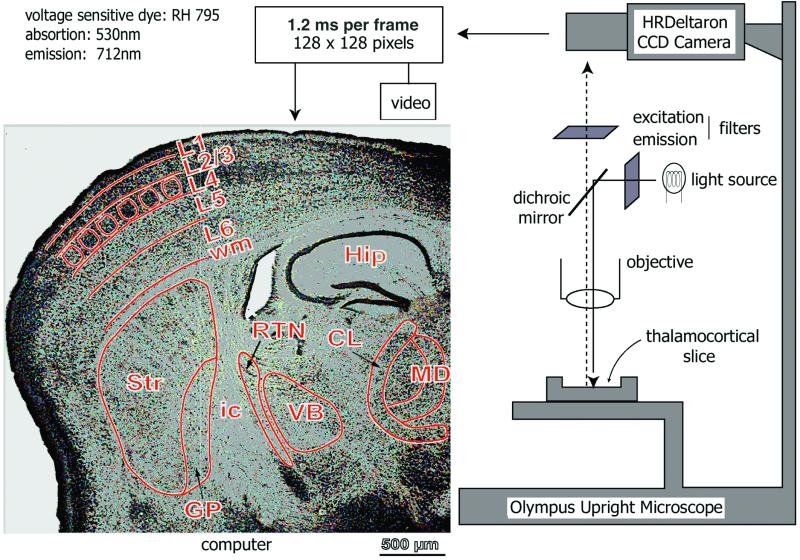
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the imaging set-up. Light from a 12-V halogen source was passed through an excitation filter (515 ± 35 nm), dichroic mirror, and microscope objective (×5) before reaching the slice stained with the voltage-sensitive dye RH-795. Emitted fluorescent light was projected onto a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera after passing through the objective, dichroic mirror, and cut-off filter (>590 nm). The CCD camera (HR Deltaron 1700; FUJIX) consisted of 128 × 128 pixels, and each pixel collected light from a surface of about 39 μm × 39 μm. Images were sampled every 1.2 ms. The optical data were analyzed off-line with matlab-based software. A low-magnification, Nissl-stained image of a thalamocortical slice (50-μm thickness) is shown at left. Nuclei and layer subdivisions were demarcated in green lines. Dorsal is up. Hip, hippocampus; ic, internal capsule; Str, neostriatum; VB, ventrobasal nucleus; CL, centrolateral; MD, mediodorsal; wm, white matter; L1, 2/3, 4, 5, 6, different cortical layers. Borders of the cortical “barrels” are demarcated.