Figure 3.
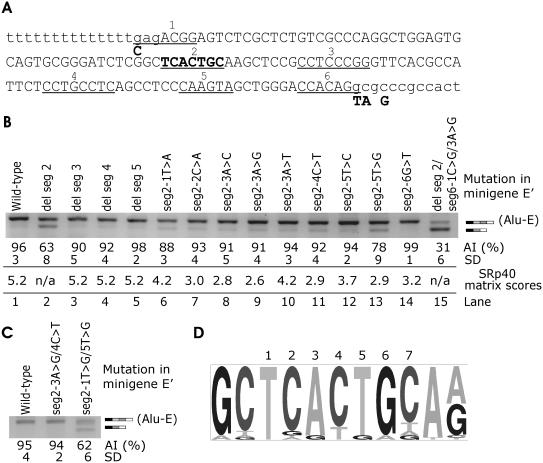
Identification of a splicing enhancer element in ACE intron 16 AluYa5 Influence of segments 2–5 deletions and segment 2 point mutations on Alu exonization. (A) Exonized Alu segment (upper case) with putative ESEs (underlined and numbered 1–6). Segments 1, 2 and 6 were predicted by the ESE Finder (8), segments 1 (C allele only), 3 and 4 were significant ESEs identified through octamer sequences (9) and segment 5 was predicted by the RESCUE-ESE (7). Intronic sequence is in lower case. To facilitate mutagenesis, segments 2 through 5 were individually deleted in minigene E′. This minigene contained intron 16 truncation (Figure 1A) and four point mutations optimizing the splice sites (shown below the nucleotide sequence in bold). A segment 2, which was mutated individually in each position, is in the middle of the sequence in bold. (B) Alu inclusion levels following deletions of segments 2–5 and point mutations in segment 2. Transfection of all splicing reporters was into 293T cells. AI, Alu inclusion. (C) Alu inclusion levels in double mutants of minigene E. (D) Consensus sequence of segment 2 heptamer in alternatively spliced exons containing right arms of antisense Alus as identified previously (34). Representation of each heptamer position (numbered above) and flanking sequences was visualized using a pictogram utility available at http://genes.mit.edu/pictogram.html.